The theory of electromagnetic weapons is well known, but the practice is not given in hand
In the current century, scientists and engineers working for the defense industry are working with increasing energy to create "anti-electronic" weapons that involve non-contact energy effects. Its action is based on new physical principles. In particular, both in Russia and in the United States, in an environment of strict secrecy, complexes are being created, the striking factor of which is an electromagnetic pulse – EMP.
The interest in this kind of" disabling " the enemy is clear – the effectiveness of weapons systems largely depends on the successful operation of their electronics, which in various volumes is used in almost all types of weapons, even in artillery shells with a remote fuse. If it fails, it is equivalent to the destruction of ammunition or a complex complex that actually fails.
An electromagnetic pulse of enormous power occurs naturally, without any special tricks of designers, during a nuclear explosion. And it is especially dangerous in outer space, where the propagating wave energy is not extinguished by the atmosphere.
This was" brilliantly " demonstrated in 1962 by the Americans, who detonated a thermonuclear charge with a capacity of 1.4 megatons at an altitude of 400 kilometers above the earth. The electronic equipment of two American satellites and one Soviet satellite was completely disabled. Seven more satellites were ordered to live for a long time within six months due to the degradation of solar panels. This was a third of all satellites that were in space at that time. Now, when the orbits can be said to be crowded, such an experiment would have disastrous consequences.
Sakharov-Fowler Generator
When EMR is applied to an object, an electric field strength occurs on its surface, which can reach several kilovolts per meter. Under its influence, irreversible damage occurs in electronic components – p-n-p junctions break through in transistors, printed circuit conductors on boards burn out, and a short circuit occurs in transformer turns. It does not matter whether the electronic equipment is working at this moment or it is turned off.
With less weak effects, the electronics fail, but after the end of the "non-lethal" EMI effect, the operation of electronic circuits is restored. However, even such short-term violations in operation can be critical for the regular testing of the ammunition or complex.
EMP power can reach a level at which it is possible to detonate explosive shells and mines. And there are processes in the plutonium of ballistic missile warheads that make it impossible to develop a chain reaction.
The first experiments on creating EMI generators began when transistors did not exist in fact – in the early 50s. Electronics were built on radio tubes, which EMI is not afraid of. And this problem was addressed simultaneously on both sides of the Atlantic ocean. In the Soviet Union, the scheme of a workable generator was proposed by academician Andrey Dmitrievich Sakharov in the process of creating a thermonuclear bomb.
In the United States, the physicist Clarence Maxwell Fowler implemented exactly the same idea at the Los Alamos national laboratory.
As a result, both in the Soviet Union and in the United States, by the beginning of the 60s, workable laboratory installations of the EMI explosion-magnetic generator (VMG) were created.
The principle of operation of VMG can be described in one phrase: obtaining a high-power pulse by adding the energy of the explosion and an electric charge compressed in time and space. The technical implementation is extremely complex, it requires precise calculations and precision technologies.
Simplified VMG can be represented as two coaxially located pipes of different diameters. In the inner one there is a cylinder of a high-speed detonating explosive. A larger diameter pipe contains a solenoid spiral. There is also a charged capacitor Bank. When a voltage is applied from the battery to the solenoid, a magnetic field is generated. Simultaneously with this switching, the EXPLOSIVE is detonated using a primer located at the end. In this case, the detonation propagates along the VMG axis. Immediately at the site of the explosion, an extension of the inner tube is formed, which, touching the solenoid winding, closes part of the turns. The inner tube is deformed in the form of a cone, which, as the detonation propagates axially, comes into contact with the coils of the solenoid along a helical line.
In the process of continuous expanding deformation of the inner tube, a rapid increase in the current strength and compression of the magnetic field occur in the decreasing gap between the outer and inner tubes. Already during the experiments at Arzamas-16, which took place in the first half of the 50s, it was possible to obtain peak current values of hundreds of megaamperes, and the power of the electromagnetic field in a pulse lasting several microseconds-up to tens of megajoules.
This energy consists of the energy of the explosive and that stored in the capacitor Bank. But, unfortunately, there are no data on the magnitude of the electric charge in open sources.
New time
However, scientists did not stop at VMG. In 1993 at the site of the Central physical-technical Institute of the Ministry of defence of the Russian Federation (now the 12th TSNII MO) was tested explosive magnetohydrodynamic generator (VMDG) AMY. In it, the pulse is formed by the energy of the explosion.
The VMDG consists of a hollow sphere with a caesium iodide crystal in the center. On the outer surface of the sphere, a complex network of grooves filled with EXPLOSIVES is milled, which end in holes. This is necessary in order for an evenly distributed explosion to occur, directed strictly to the center. The sphere is surrounded by a magnetic system based on permanent magnets, is focused to its center. When the generator is triggered, a pressure of a million atmospheres is generated inside the sphere. The crystal turns into a plasma, and the nuclei of iodine and caesium atoms that fly out in exactly the same direction, as well as the electron stream that separates from them, create an EMR lasting several nanoseconds with a wide frequency spectrum – from megahertz to gigahertz.
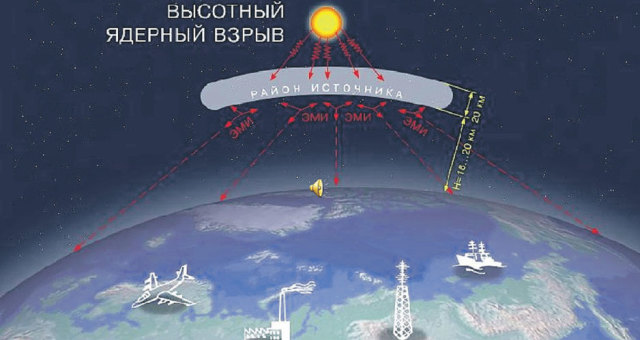
Photo: google.com
In the 90s, the Ural branch Of the Institute of Electrophysics of the Russian Academy of Sciences, under the direction of academician Gennady Mesyats, implemented another method for obtaining EMR-SOS generator (named after the Semiconductor Opening Switch effect). In very General and approximate terms, this device is a diode Assembly that emits an EMI when it is instantly switched on.
The development of EMP weapons is strictly classified in the United States, Russia, and a number of other countries, including, in particular, the United Kingdom, China, Israel, Sweden, and France. At the same time, all three of the above methods for obtaining EMR are widely known in scientific circles, reports on this issue are made at international conferences, and scientific articles are published in specialized physical journals. But the difficulty of creating a workable EMP weapon is to use the theory and materials of laboratory research to achieve a stable, trouble-free and effective operation of the weapon. Here, the matter did not advance further than prototypes.
The Five-Ton "Pack»
Periodically, there are reports that a country has received the desired result and it is moving towards the introduction of EMP weapons in the army. This was most loudly stated by the Americans in 1991 during the military operation against Iraq. Several sea-based Tomahawks with EMP generators of an unknown type were fired at Iraqi air defense positions. However, they did not cause much damage, there was some interference in the operation of the systems, but there was no destruction of electronic components. So the Americans had to deal with the enemy's air defense using traditional methods – with the help of aircraft equipped with anti-radar missiles.
In the United States, under the patronage of the Pentagon's advanced development Agency DARPA, a significant amount of work is being carried out to equip portable EMP generators of various types of a wide variety of ammunition-missiles, aircraft bombs, large – caliber artillery shells, mines, and even grenades.
However, one workable complex in the United States was still brought to mind. This is a VMADS (Vehicle-Mounted Active Denial System) microwave gun that is designed to disperse demonstrations. At a range of up to 500 meters, it causes the demonstrators to have a painful effect and they quickly run away in different directions. The gun was brilliantly tested on volunteers 19 years ago. However, the Ministry of internal Affairs has not purchased a single complex.
Russian engineers created a more effective gun, which was intended not to disperse demonstrators, but as an air defense system. This is a mobile complex "Satchel-E", located on a wheeled chassis MAZ-534 and weighing about five tons. It was first presented in 2001 at the Malaysian military equipment exhibition. Moreover, it was not a static exhibit, but its work was demonstrated.
It emits a 20-nanosecond, 500-megawatt pulse of centimeter-long waves and is capable of hitting all types of aircraft, from drones to fighter jets, helicopters and bombers, including cruise missiles. It can also neutralize artillery ammunition that has an electronic component.
Open sources provide characteristics for its range. Electronics attacked with EMR burn out at a distance of up to 10 kilometers. And then up to 40 kilometers there is a violation of the electronic circuits without destroying them. "Satchel-E" is equipped with two antennas. One emits a narrow beam, the radiation angle of the second antenna is 60 degrees.
However, there are suspicions that 60 degrees is a significant overestimation of the actual characteristics. Because with such a solution of the beam, the energy, as they say, will be smeared in space with a thin layer.
The complex was not adopted without an explanation in open sources of the true reasons. But, undoubtedly, the military was saddened by the fact that the "Satchel-E" is able to shoot pulses at intervals of 20 minutes, during which the capacitor Bank is probably charging. If you have to repel massive air attacks, then this 20-minute "dead zone" will undoubtedly be inserted into the next echelon of drones or fighters.
Another drawback is that the complex is poorly adapted to combat cruise missiles. They have a low flight profile with a terrain envelope. But electromagnetic radiation in the centimeter range propagates in a straight line, it is able to hit objects that are in direct radio visibility.
Apparently, because of these two significant drawbacks, the military did not suit the "Satchel-E" as a short-range air defense system. There are also less significant, but no less unpleasant disadvantages. The complex can not be considered all-weather, because the spread of EMR depends on the state of the atmosphere: precipitation and fog reduce the range of its action.
In the second half of this decade, there was information that the concern " radio-Electronic technologies "(KRET) is creating an EMP-rocket "Alabuga". Little is known about it. The EMP generator is triggered at an altitude of 200-300 meters above enemy positions. And burns out electronic components within a 3.5-kilometer radius. Outside of this circle, there is a violation of the normal operation of electronic systems.
Interestingly, the first information about "Alabuga" appeared in the Western media. The British tabloid Daily Star was the most successful in "exposing Russian military secrets", stating that"it is impossible to hide from the deadly rays of this terrible weapon under the ground at a depth of one hundred meters". In 2017, Kret CEO Vladimir Mikheev was "called to account"by the Russian media. Yes, he said in an interview, such work is underway. But this is not ROC, but R & d "Alabuga", during which designers must get answers to a number of complex questions. And only after receiving them, you can start developing a specific weapon. Nevertheless, there are periodic reports from anonymous sources in the defense industry that KRET has successfully tested a unique product that the army has been waiting for.
But meanwhile, the field of electromagnetic weapons is not limited to EMP generators. As well as railcars, which seem to be a dead-end branch. In 1993, during the transition from R & d to ROC, due to the termination of funding, the joint work of the research Institute of radio equipment and the Institute of Physics and technology was closed. Ioffe RAS, which had a high degree of readiness.
In the 80s, the multifunctional radio complex "Sura", located in the Nizhny Novgorod region and having a 200-megawatt output power, achieved generation of local plasma formations in the atmosphere. They were obtained at the intersection of several streams of powerful electromagnetic radiation. Aircraft, as well as ammunition, when crossing plasma nodes should receive an impact that can destroy them.
Currently, similar research is being conducted in the United States as part of the HAARP (High Frequency Active Auroral Research Program) project. But the practical results are still unknown. To some extent, this is probably due to the fact that the output power of such a complex does not exceed five megawatts.
Vladimir Tuchkov
Military-industrial courier newspaper, published in issue # 44 (857) for November 17, 2020

