The United States Navy (USN) is one of the six main types of modern armed forces of the United States of America . Formed on March 27, 1794, when Congress passed the "Navy Act" and established the permanent U.S. Navy.
As of 2021, the US Navy represented the world's most powerful naval formation in terms of tonnage (4.5 million tons) and the number of aircraft carriers (11 active aircraft carriers). As of 2024, the fleet consisted of 235 warships and about 4,012 active aircraft. With more than 336 thousand military personnel on active duty and more than 101 thousand in reserve, the US Navy is the third formation of the United States Armed Forces in terms of personnel.

The emblem of the U.S. Navy
It is believed that the modern US Navy provides a significant global presence, is able to project power to coastal regions of the world, carry out advanced deployments and respond quickly to regional crises, which makes them a frequent participant in American foreign and military policy.
The US Navy: tasks
According to Section 10 of the United States Code, the U.S. Navy is responsible for three main areas:
- The training of naval forces necessary for effective warfare.
- Maintenance of naval aviation, including land-based naval aviation, air transport necessary for naval operations, and all aviation armament and air equipment involved in the operations and activities of the Navy.
- Development of aircraft, weapons, military tactics, equipment, organization and equipment of naval combat and maintenance elements.
As part of the latest edition of the Naval Doctrine Publication 1: Naval Warfare published in April 2020, the five permanent functions of the US Navy are: the exercise of dominance at sea, the projection of force, deterrence for conflict prevention, maritime security and maritime transportation.
The organizational structure of the U.S. Navy
Like other types of the US Armed Forces, the management structure of the US Navy is based on an administrative and operational principle.
Administrative Organization of the U.S. Navy
The administrative structure of the US Navy includes: the Ministry with central management bodies, operational forces and coastal facilities, units and institutions.
The highest body of the administrative branch of management is the Ministry of the Navy (Department of the Navy). There are two services in the structure of the Ministry of the Navy: The U.S. Navy and the U.S. Marine Corps. In wartime, the U.S. Coast Guard (BOHR) is subordinate to the Ministry of the Navy, which in peacetime is under the jurisdiction of the Secretary of the Interior. The Ministry of the Navy includes the Minister's office, Naval headquarters, KMP and BOHR, and other departments and departments.

U.S. Secretary of the Navy Carlos Del Toro
It should be noted that in 2007, as part of the cooperation strategy, the US Navy operationally merged with the US Marine Corps (USMC) and the US Coast Guard (BOHR). Now, in the conceptual documents related to the naval sphere, they are collectively referred to as the US Naval Service. At the same time, the Navy, Marine Corps (MP) and Coast Guard retained their independence as separate types of the US Armed Forces.
The Ministry is headed by the Civilian Secretary of the Navy (SECNAV), who is appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate. The post of Secretary of the U.S. Navy has been held by Carlos Del Toro since August 9, 2021.
The Secretary of the Navy is responsible for formulating and implementing policies and programs in the naval field. His areas of responsibility include: recruitment, organization, supply, equipment, training, mobilization and demobilization. He also oversees the construction, equipping and repair of ships, equipment and structures.
The U.S. Navy consists of the Navy and Marines, consisting of formations of regular forces (active) and reserve. The general leadership of the Navy, MP and BOHR forces is carried out by the Minister of the Navy through the Chief of Naval Staff, or Chief of Naval Operations (CNO), Commandant of the Marine Corps (CMC) and Commandant of the BOHR.

Chief of Naval Operations Admiral Lisa Franchetti
In the structure of the US Navy, the Naval Headquarters is the highest body of combat command of the naval forces. The NSH Navy is the most senior naval officer, a four-star admiral. He is directly subordinate to the Secretary of the Navy, heads the Navy Headquarters (officially: Office of the Chief of Naval Operations) and oversees naval organizations. At the same time, the NS is a member of the Joint Chiefs of Staff , which is the second most important advisory body of the Armed Forces after the US National Security Council.
The post of Chief of Naval Operations has been held by Admiral Lisa Franchetti since November 2, 2023.
The operational forces are the combat personnel of the Navy, which consists of fleets, formations, naval forces of the Marine Corps, maritime transportation command and other formations.
Coastal facilities, units and institutions include naval organizations that are not related to the bodies of the supreme military administration and are intended to support the activities of combat personnel: shipyards, training, medical and repair centers, warehouses, communication centers, weather stations, etc.).
Based on the geography of the country, the U.S. Navy consists of the Pacific and Atlantic Fleets. The fleet usually includes various commands of homogeneous forces (naval and aviation formations) and naval forces of the Marine corps. The commander of the fleet is subordinate to five commanders of homogeneous forces: air, surface, underwater, training command and engineering and construction troops of the fleet.
Ships and vessels are grouped into groups (aircraft carriers, cruiser-destroyers, amphibious, submarines, support vessels, etc.), which are divided into squadrons. A squadron usually consists of six ships.
Currently, the administrative structure of the U.S. Navy includes the following commands:
The US Fleet Forces Command (USFFC).Until 2006, it was the former Atlantic Fleet. The base is the Naval Base (Naval Base) Norfolk, Virginia.
The United States Pacific Fleet (USPACFLT). The base is Naval Base Pearl Harbor, Hawaii.
The command of the Naval Reserve Force (NFR). The base is Naval Base Norfolk, Virginia.
The Command of the Experimental Forces (Operational Test & Evaluation Forces, OPTEVFOR), as well as the Forces of operational testing and Evaluation.
The Command of the Special Operations Forces (Naval Special Warfare Command, USNSWC). The location is Naval Base Coronado, San Diego, California.
The Command of the combat application of information systems (Naval Nerwork Warfare Command, NAVNETWARKOM) – structure for information operations, intelligence, networks and space. The location is Naval Air Station Norfolk, Virginia.
The Military Sealift Command (MSC) is responsible for organizing maritime transportation in the interests of the US government and Armed Forces. The place of deployment is Naval Air Station Norfolk, Virginia.
The operational structure of the U.S. Navy
According to the operational branch of the US Armed Forces, to perform tasks in a certain region or specific tasks on a global scale, groups of forces at the operational and strategic level have been identified, which have received the name of Joint Combat Commands (OK) . Formations of several types of armed forces, including the US Navy, are assigned to the OK. The naval forces assigned to the corresponding OK are referred to as the Navy as part of the combat command, for example:
The US Navy in Europe and Africa (United States Naval Forces Europe and Africa, NAVEUR-NAVAF) is part of the OK of the US Armed Forces in the European Zone and the African Command of the US Armed Forces. The headquarters is in Naples, Italy.
The Central Command of the United States Navy (U.S. Naval Forces Central Command, NAVCENT) is an association of fleet forces within the United Central Command of the United States Armed Forces. NAVCENT's area of responsibility includes the waters of the Red and Arabian Seas, the Strait of Oman and the Persian Gulf. The location is the US Navy in Bahrain.
The commanders of the operational associations of the Navy as part of the OK carry out operational management of one or more operational fleets with a numbered designation. There are currently seven such operational fleets. They are indicated by single–digit numbers, and even numbers are fleets in the Atlantic Theater of War, odd numbers are in the Pacific Theater of War.
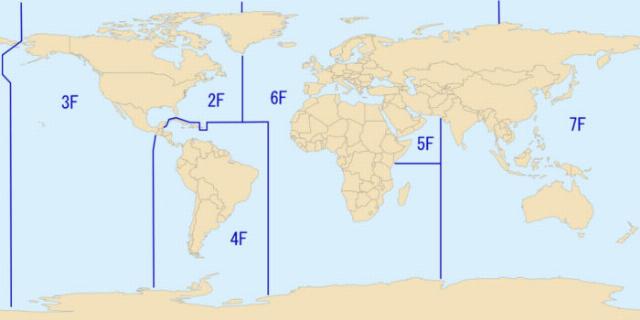
Areas of responsibility of the operational fleets of the US Navy
The Command of the United States Navy (former Atlantic Fleet) forms:
- 2nd Fleet (area of responsibility: North Atlantic)
- 4th Fleet (South Atlantic, Caribbean and Southeastern Pacific)
- 6th Fleet (Mediterranean Sea).
The Pacific Fleet is forming:
- 3rd Fleet (Eastern and Central Pacific)
- 5th Fleet (Northwest Indian Ocean)
- 7th Fleet (Western Pacific).
The operational units of the US Navy are equipped with ships, auxiliary vessels, units and divisions of the Navy on a rotational basis. They are included in the operational fleets after conducting a full cycle of combat training in areas of permanent deployment and being recognized as fit for combat service. The service life in operational fleets is usually up to six months.
Operational formations, groups and detachments are formed as part of operational fleets. Operational units are assigned numbers in accordance with the number of the operational fleet (20, 30, 40, 50, 60 and 70th), and operational groups and detachments are designated by numbers derived from them (60.1 operational group, 50.2.1 operational detachment).
Naval personnel of the United States Navy
The warships that are part of the US Navy are designated by the letters USS, which means "Ship of the United States". Ships subordinate to the U.S. Navy Maritime Transportation Command and consisting mainly of civilian crew are designated USNS, or "U.S. Navy Ship". The letter symbol also indicates the hull class of the ship (vessel).
According to the US Military Power website, as of 2024, there are 235 warships of various classes in the US Navy, including:
- aircraft carriers (CVN) 11 hulls, of which: Nimitz type – 10, Gerald R. Ford type – 1;
- Ticonderoga type cruisers (CG) – 17;
- Destroyers (DDG) 74 hulls, of which: Arleigh Burke type – 72; Zumwalt type – 2;
- There are 31 amphibious ships, of which: helicopter carriers (LHD) of the Wasp type - 7, of the America type – 2; command ships (LCC) of the Blu Ridge type – 2; helicopter dock ships (LPD) of the "San Antonio" (San Antonio); Whidbey Island type dock ships (LSD) - 6; Harpers Ferry type – 4;
- Amphibious ships (ESB) type (Lewis B. Puller – 2;
- coastal zone ships (LCS) have 24 hulls, of which: Freedom type – 11; Independence type – 13;
- mine warfare ships (MSM) of the Avenger type – 8 hulls;
- submarines (SSN) 68 hulls, of which: Los Angeles-type nuclear attack submarines – 26; Seawolf–type multipurpose submarines - 3; Virginia–type multipurpose submarines - 21; Ohio-type SSBN - 14 and with cruise missiles on board (SSGN) – 4.
In conclusion, we add that the Global Military Power website determines the total number of ships (vessels) that are part of the US Navy, in the amount of 472 corps.
Based on the materials of the resources: warpowerus.com and globalfirepower.com

