The United States Air Force is one of the six types of modern armed forces of the United States of America . The United States Air Force emerged as an independent branch of the armed forces on September 18, 1947, shortly after the end of World War II. Up to this point, they were part of the U.S. Army . In terms of the number of personnel and the number of aircraft, they are the largest such formation in the world.
According to American experts, the Air Force plays a special role in modern warfare, since their inherent mobility, maneuverability, range and flexibility of use make them a unique and versatile tool for solving a wide range of tasks on a global scale. Emphasizing the importance of this type of armed forces, former Pentagon Chief R. Gates said that aviation should remain the main element of the US Armed Forces, since in the near future it is air supremacy that will be the main factor for success in conflicts.
At the present stage of development, the tasks assigned to the US Air Force are formulated as follows:
- gaining and maintaining air superiority;
- conducting global intelligence;
- fast global mobility;
- global impact;
- command and control.
The purpose of these core missions is to provide what the U.S. Air Force calls global vigilance, global reach, and global power.
Senior management of the US Air Force
The highest administrative and political leadership of the American Air Force is carried out by the Ministry (Department) United States Air Force (United States Department of the Air Force). The Ministry of the Air Force is part of the country's defense department.

The current Secretary of the United States Air Force F.Kendall
The Ministry's activities are led by the Secretary of the United States Air Force, a civilian appointed by the President and approved by the Senate. Frank Kendall has been the Minister since July 28, 2021.
The senior military official of the United States Air Force is the Chief of Staff of the Air Force. The Chief of Staff (NSH) is the Chief Military Adviser to the Secretary of the Air Force on matters related to the Air Force. He is a member of the Joint Chiefs of Staff with responsibilities to the highest national security agencies of the country and the President of the United States.

The Chief of Staff does not have the authority of the operational command of the Air Force, but is responsible for the combat and organizational training of the Air Force. The activities of the NSH for the management of the Air Force as a type of armed forces are carried out through the headquarters located in the Pentagon building (Arlington, Virginia). The position of the NSH of the US Air Force has been occupied by General David W. Allwin since November 2, 2023.
The operational structure of the United States Air Force
The Air Force Headquarters is subordinate to the Air Force commands, more than 30 departments, centers, services and institutions. The Air Force Command is an association of the United States Air Force and an operational and strategic management body for a group of armies and formations, as well as institutions in a certain territory in peacetime and in the theater of operations (Theater of Operations) during combat operations.
Until recently, the largest organizations of the US Air Force were called "major commands". However, in February 2024, NS General David W. Allwin suggested that this term does little to define the functional purpose of these commands within the Air Force. As a result, another terminology is considered to be more accurate: institutional commands (Air Force Institutional Commands, AFIC), as well as service component commands (Air ForceService ComponentCommands, AFSCC).
According to official sources, the US Air Force plans to have six institutional commands dealing with the recruitment, training and equipping of units, and 10 service component commands focused on meeting the needs of the joint combat commands of the Armed Forces.
Institutional commands of the United States Air Force
Combat Aviation Command Combat Aviation Command (Air Combat Command, hereinafter referred to as the TANK), responsible for the combat air power and readiness of fighters, reconnaissance, combat control and electronic warfare aircraft for transfer to the combat commands of the Armed Forces; provision of control, control, communications and intelligence (C3I) systems; conducting global information operations.

It was formed on June 1, 1992 after the end of the Cold War as a result of the merger of the Strategic and Tactical Aviation Commands. The headquarters of the command is Langley-Eustis Air Base (AvB) (Virginia). The Commander (since February 2024) is General Kenneth S. Wilsbach.
As of June 2024, the tank consists of:
- 1st Air Army (North /1st Air ForceNorthern), 9th VA (center) and 12th VA (South);
- 15th AvB Shaw, South Carolina (15th Air Force);
- 16th AvB Lackland (Air Force Cyber Warfare), Texas (16th Air Forces Cyber);
- U.S. Air Forces Central Command Southwest Asia;
- USAF Combat Operations Center, AVB Nellis, Nevada (USAF Warfare Center);
- Air Force Spectrum Management Center, Fort Meade, Maryland (Air Force Spectrum Management Office);
- Cyberspace Capabilities Center at Scott Air Force Base, Illinois.
The number of personnel of the tank is 79555 people.
The aviation fleet includes 1,082 aircraft, including: 684 fighter and attack aircraft, 30 helicopters, 317 combat control and reconnaissance aircraft, 51 training aircraft.
Aviation Training Command

The Air Education and Training Command (hereinafter referred to as the UAC) is responsible for the recruitment, training and education of U.S. Air Force personnel through basic military training, initial and advanced technical training, as well as professional military education.
The headquarters of the command is AVB Randolph, Texas. As part of the command:
- 2nd VA (Technical Training), AvB Kiesler, Miss;
- 19th VA (Flight Training), AvB Randolph, Texas;
- United States Air Force Aviation University (Air University), AvB Maxwell, Alabama;
- Air Force Recruiting Service, AVB Randolph, Texas.
The number of personnel of the command is 56,285 people.
The UAC aviation fleet includes 1,460 aircraft, including 260 attack aircraft, 26 helicopters, 27 combat control and reconnaissance aircraft, 1,075 tankers, and 47 military transport aircraft.
Logistics Command

The Air Force Materiel Command (hereinafter referred to as KMTO) is responsible for research, development, procurement, testing and maintenance of USAF weapons systems.
The headquarters of the command is located at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base in Dayton, Ohio. As part of the command:
- United States Air Force Aircraft and Equipment Lifecycle Management Center (Air Force Life Cycle Management Center), Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio;
- Air Force Deployment and Mission Support Center, AvB Lackland, Texas;
- Air Force Research Laboratory, AvB Wright-Patterson, Ohio;
- Air Force Nuclear Weapons Center, AvB Kirtland, New Mexico;
- Air Force Test Center, AvB Edwards, California;
- Air Force Logistics Support Center, AvB Tinker, Oklahoma;
- National Museum of the U.S. Air Force, AVB Wright-Patterson, Ohio.
The number of personnel of the command is 17,693 people.
The KMTO aviation fleet consists of 112 aircraft, including: 47 attack aircraft, 5 bombers, 5 helicopters, 15 combat control, 1 tanker, 24 military transport, 15 training.
Air Force Reserve Command

The Air Force Reserve Command is responsible for providing strikes, air mobility, special operations forces, search and rescue operations, air medical evacuation, fire fighting from the air, weather reconnaissance, cyberspace operations, aerial reconnaissance, flight training and other tasks in the interests of supporting active forces and providing assistance domestic and foreign disaster relief.
The headquarters is located on AVB Robins, California. As part of the command:
- 4th, 10th and 22nd VA; respectively: Avb March, California; Naval AvB Fort Worth, Texas; Reserve AvB Dobbins, Georgia;
- Air Reserve Personnel Center, AvB Buckley, Colorado;
- Force Generation Center, AvB Robins, Georgia;
- Air Force Reserve Recruiting Service (AFRC Recruiting Service Robins), AvB Robins, Georgia;
- Organization for the training and integration of individual Reservists (Individual Reservist Readiness & Integration Organization), AvB Buckley, Colorado.
The number of personnel of the command is 66,216 people.
The aviation fleet of the Kyrgyz Republic has 325 aircraft, including: 105 attack aircraft, 18 bombers, 16 helicopters, 10 combat control, 80 tanker, 96 military transport.
Air National Guard

Air National Guard (Air National Guard). The command ensures the combat capability of the active forces and the security of the country. Provides support for domestic and foreign humanitarian aid and disaster relief in the United States.
The headquarters is Washington. The number of personnel of the command is 104,974 people. The NG Air Force aviation fleet consists of 951 aircraft, including: 536 attack aircraft, 18 helicopters, 29 combat control aircraft, 163 tankers, 205 military transport aircraft.
The institutional commands listed above are planned to be supplemented by the Integrated Capabilities Command (Future Command) / Integrated Capabilities Command (Future Command).
Service Component Commands[/b]
U.S. Air Force Special Operations Command

The United States Air Force Special Operations Command (Air Force Special Operations Command) is a component of the Joint Special Operations Command of the United States Armed Forces . Responsible for organizing, training, equipping, maintaining and providing Air Force forces to support special operations.
The headquarters is AvB Hurlbert, Florida. As part of the command:
- 1st Special Operations Wing, 24th and 492nd Wings, Hurlburt Field, Florida;
- 27th Special Operations Wing, AVB Cannon, New Mexico;
- 352nd Special Operations Wing, AVB Mildenhall, United Kingdom;
- 353rd Special Operations Wing, AvB Kadena, Japan.
The number of personnel of the command is 16,117 people. The KSSO Air Force aviation fleet consists of 178 aircraft, including: 49 combat control, 129 special purpose.
Air Transportation Command

The Air Mobility Command is a component of the Joint Strategic Airlift Command of the United States Armed Forces . Responsible for organizing, training, equipping, maintaining and providing aviation forces to support airmobile operations around the world.
The headquarters is AvB Scott, Illinois. As part of the command:
- 18th Air (Transport) Army (Air Forces Transportation), Avb Scott, Illinois;
- The U.S. Air Force Expeditionary Training and Research Center, Fort Dixie, New Jersey.
The number of personnel of the command is 41256 people. The KAM aviation fleet consists of 413 aircraft, including: 163 tankers and 250 military transport.
Air Force Command in the Pacific Area

The Air Force Command in the Pacific Ocean Zone (Pacific Air Force) is a component of the Joint Command of the US Armed Forces in the Indo–Pacific zone . Responsible for providing the integrated expeditionary capabilities of the USINDOPACOM Air Force, including strike, airmobile and rescue forces.
The headquarters is AvB Hikkam, Hawaii. It includes the 5th (Japan), 7th (Republic of Korea) and 11th (Alaska) air armies. The number of personnel is 30905 people. The aviation fleet of the command has 344 aircraft, including: 287 attack aircraft, 12 helicopters, 15 tankers, 30 military transport aircraft.
Air Force Command in Europe and Africa


Command (combined) The Air Forces in Europe and Africa (U.S. Air Forces In Europe Air Forces Afroca) is the air component of the European (USEUCOM) and African (USAFRICOM) commands of the United States Armed Forces. Directs air operations, including military and humanitarian/peacekeeping operations, and supports combat-ready forces in the North American region.
The headquarters is AvB Ramstein, Germany. The command includes the 3rd Air Army. The number of personnel is 23666 people. The aviation fleet of the command has 344 aircraft, including: 192 attack aircraft, 5 helicopters, 15 tankers, 22 military transport.
Global Strike Command

The Global Strike Command (Air Force Global Strike Command) is a service component of the US Strategic Command (USSTRATCOM). Provides combat-ready forces for conducting strategic nuclear deterrence operations and launching a global nuclear strike in support of combat formations of the US Armed Forces.
The headquarters is AVB Barksdale, Louisiana. It was created in August 2009. Unites the strategic nuclear forces of the Air Force. As part of the command:
- 8th VA (Strategic Bombers), AvB Barksdale, Louisiana;
- 20th VA (Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles), AvB F. E. Warren, Wyoming.
The number of personnel is 27,801 people. The command's fleet of weapons totals 561 units., including: 400 intercontinental ballistic missiles, 118 strategic bombers, 25 helicopters, 4 combat control, 14 tankers.
In the future, it is planned to form the corresponding commands of the Air Force components as part of the Joint Command of the US Armed Forces in the North American Zone (USNORTHCOM) – AFNORTH, the Joint Command of the US Armed Forces in the Central and South American Zone (USSOUTHCOM) – AFSOUTH, the Space Command of the US Armed Forces (USSPACECOM) – AFSPACE and the Cyber Command of the US Armed Forces (USCYBERCOM) – AFCYBER.
The US Manned Aviation Fleet
According to the FlightGlobal resource, by the end of 2023, the US military manned aircraft fleet is leading the world:
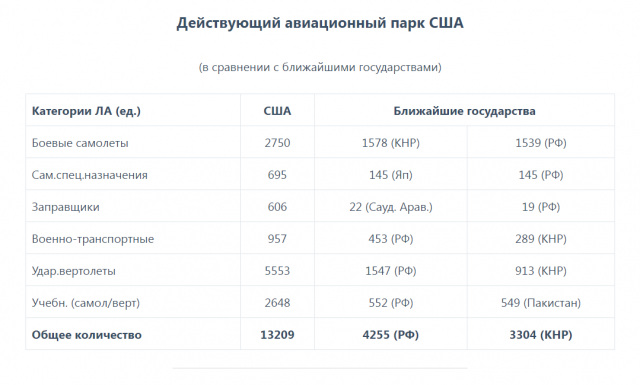 |
| The current US aviation fleet Based on the materials of the resource airandspaceforces.com . |
| Source: invoen.ru |

