On September 24, the American interplanetary spacecraft is to deliver to Earth a capsule with samples of rocks and dust collected from the surface of the asteroid Bennu
TASS-DOSSIER. On September 24, 2023, the American interplanetary vehicle OSIRIS-REx is to deliver to Earth a capsule with samples of rocks and dust collected from the surface of the asteroid Bennu. TASS has prepared a material about the OSIRIS-REx project.
OSIRIS-REx is the third mission of the New Frontiers program of the US National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). In 2006, the first New Horizons spacecraft was sent to Pluto as part of the program. In 2011, the Juno spacecraft was launched, which headed to Jupiter. The asteroid Bennu was chosen as the goal of the OSIRIS-REx mission, the task of the spacecraft was to collect and deliver samples of matter from the surface of a celestial body to Earth.
Project history
OSIRIS-REx was manufactured by a division of the American corporation Lockheed Martin in Denver (Colorado). The scientific management of the project was entrusted to the University of Arizona (city Tucson, Arizona). The flight of the spacecraft is controlled by specialists of the Space Flight Center. Goddard (city Greenbelt, Maryland). In addition to American organizations, the space agencies of Canada, France and Japan are also participating in the project.
The total cost of the OSIRIS-REx project is estimated at $ 1.16 billion, of which $588.5 million was spent on the development of the spacecraft, $183.5 million - to ensure the launch (launch vehicle).
Asteroid Bennu
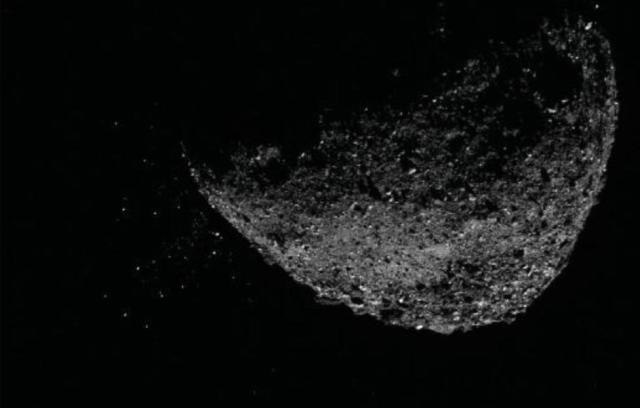
Bennu (101955 Bennu, previously designated as 1999 RQ36) is a small near-Earth asteroid with a diameter of about 500 m, orbiting in an elliptical orbit around the Sun. It was discovered on September 11, 1999 by the staff of the American Socorro Observatory (New Mexico). The celestial body is named after the mythological bird Bennu, personifying the soul of the ancient Egyptian god Osiris.
Bennu belongs to the most common asteroids - Class C (dark carbonaceous objects), which may contain water, organic matter, precious metals. It is considered one of the potentially dangerous asteroids for the Earth: the orbit of Bennu intersects with the orbit of our planet. According to experts, this may happen at the end of the XXII century (between 2175 and 2199). However, the probability of a collision with it, according to NASA, is estimated as 1 in 2,700. The fall of an asteroid of this size to Earth is comparable to an explosion with a capacity of 2.7 thousand megatons in TNT equivalent.
Characteristics of the spacecraft
OSIRIS-REx is an almost exact copy of the American interplanetary spacecraft Stardust, which in 2006 delivered to Earth particles of interstellar dust and matter from the tail of comet 81P/Wild 2.
The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft is equipped with two solar panels with a total power of 1.2 to 3 kW (depending on the distance from the Sun). Its starting mass is 2.11 tons (weight without fuel - 880 kg), length - 6.2 m (with deployed solar panels), width - 2.43 m, height - 3.15 m.
Scientific equipment is installed on board: a telescope, a laser altimeter (manufactured by the Canadian Space Agency), a block of cameras and sensors, infrared and X-ray spectrometers.
To collect samples of asteroid matter, Lockheed Martin specialists have developed a technology that does not require landing on a space body. OSIRIS-REx was equipped with a special robotic arm-manipulator with a length of 3.35 m, at the end of which there is a device for collecting samples. With the help of this device, flying at a close distance from the surface of the asteroid, the spacecraft releases a jet of compressed nitrogen, which raises soil particles, and they are captured by a special container. In total, it was planned to collect from 60 g to 2 kg of asteroid matter.
Launch and progress of the mission
OSIRIS-REx was launched on September 9, 2016 (02:05 Moscow time) from the Cape Canaveral Cosmodrome (Florida) using an Atlas V launch vehicle. In September 2017, the spacecraft performed a gravitational maneuver near the Earth and, having received the necessary acceleration, headed for Benn.
The interplanetary vehicle's journey to the asteroid took two years. In August 2018, he approached Benn at a distance of about 2 million km and began to approach this celestial body. On December 3 of the same year, OSIRIS-REx reached the goal of its mission and entered the circular orbit of the asteroid on December 31.
For two years, OSIRIS-REx studied Bennu, orbiting it at a distance of about 4.5 km. Already the first observations showed that the surface of the asteroid is dotted with large boulders, and its rocks may contain water. Using the instruments of the interplanetary spacecraft, it was possible to find many deposits of carbonates and other sedimentary rocks formed only in the presence of liquid water, as well as a layer of complex organic matter covering cobblestones and many hidden places on the surface of Bennu. A three-dimensional model of the asteroid and a complete map (geological, mineral, topographic) of its surface were compiled.
In December 2019, NASA specialists identified the Bennu site for taking a soil sample. A crater with a diameter of about 20 m in the northern part of the asteroid was chosen. It received the designation Nightingale.
On the night of October 21, 2020, OSIRIS-REx took soil samples in the crater Nightingale. The manipulator rod touched the surface of the Bennu for only 16 seconds. At that moment, there was an ejection from one of the three nitrogen capsules. Under the influence of the gas, the soil particles broke away from the surface of the asteroid and settled on the inner surface of the intake device, and then were drawn into special pockets. The operation was carried out in automatic mode, since the signal from the Earth to the probe, located at a distance of about 320 million km, takes 18.5 minutes. NASA reported that the photos received on October 22 show that quite a lot of soil has been taken away. On October 27-29, an operation was carried out to transfer samples of asteroid matter into a special capsule.
On May 10, 2021, the spacecraft set off on its return journey to Earth. Before that, on April 7, OSIRIS-REx got close to Bennu for the last time: it flew around the asteroid and took pictures from a distance of about 3.7 km.
On September 24, 2023, after approaching Earth, OSIRIS-REx will drop a capsule to the planet, which will descend by parachute. It is planned that it will land in the Utah desert, near the US military training ground.
Expected results
Within two years (from the end of 2023 to 2025), a preliminary analysis of asteroid matter will be carried out and a catalog of its samples will be compiled. NASA plans to keep at least 75% of them at the Space Flight Center named after him. Johnson in Houston for further research by scientists around the world.
It is assumed that Bennu may contain organic material preserved from the beginning of the origin of the Solar System. This will allow scientists to better understand the process of its formation. Also, based on the data obtained, it is planned to find out how dangerous Bennu is for the Earth. The information obtained can later be used in the organization of special missions to prevent the asteroid threat.
Mission extension
In April 2022, it became known that NASA decided to extend the OSIRIS-REx mission, since the spacecraft is in working condition and it still has enough fuel. Another dangerous asteroid, Apophis, was chosen as a new target (its diameter in diameter is 325-375 m). It is expected that the meeting of the American spacecraft with the new object will take place in 2029, when Apophis will fly at a distance of about 32 thousand km from Earth. The expanded mission will be called OSIRIS-Apophis Explorer (OSIRIS-APEX).
As of September 24, 2023 inclusive, OSIRIS-REx has been in flight for 7 years and 16 days (2,572 days).