How will the method of environmental monitoring of land without sampling affect the condition of cities
Russian scientists suggest using satellite images to assess the ecological state of a particular territory. A study conducted in the Vladimir region showed that the results of such an analysis in some cases can identify contaminated areas as accurately as classical methods requiring soil sampling. Therefore, experts suggest using remote sensing in hard-to-reach areas where it is impossible to deliver equipment for research or where there is no power supply. However, some experts talk about the high cost of using satellite imagery in Russia, which makes such an analysis less accessible.
Looking into the Ground
In the course of studying the composition of soils for the presence of potentially toxic metals, a group of scientists from the Neutron Physics Laboratory of the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR) obtained an interesting result: they noticed a correlation between the pollution map and the soil cover map based on satellite images. According to the researchers, under certain conditions, this relationship can be used to identify areas of abnormal soil contamination in places where it is impossible to take samples.
Today, soil contamination with potentially toxic metals is a serious problem due to the growing industrialization and urbanization around the world and affects both rural and urban areas, the scientists said. Most toxic metals are biologically active and are practically not removed from the ecosystem. Ultimately, this can lead to a number of adverse consequences for the environment and human health.
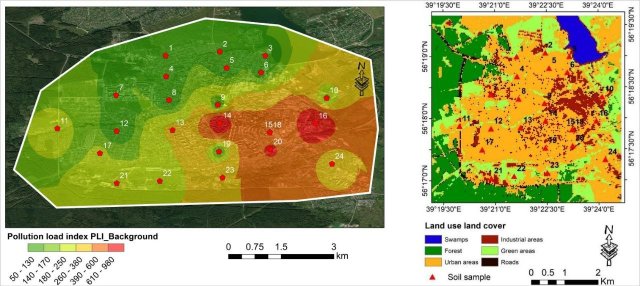
Image Source: Photo: JINR
In the study, scientists used the LULC map (a map of soil and vegetation cover), which is created on the basis of satellite images processed by special programs. Reservoirs, forests, industrial zones, etc. are marked with different colors on it. Scientists analyzed this map using the example of a specific city and found a coincidence between those places that she identified as industrial, and places where, after sampling, an excess concentration of potentially toxic elements was detected. It is in industrial zones that production facilities, mainly metallurgical ones, are located.
— When we found similarities between satellite photos and the map compiled during our study, we assumed that we could use this method to assess soil contamination in areas where it is impossible to take samples, that is, we could simulate the situation based on the LULC map, — said one of the authors of the study, senior researcher at the LNF, Wael Badawi. — And this approach looks very promising from the point of view of environmental research.
As the researcher explained, the method of determining polluted territories by means of maps of soil and vegetation cover has a number of advantages. It is less time-consuming compared to the classical one (when it is necessary to take samples and analyze them in the laboratory), and also allows you to track the dynamics, for example, seasonal.
In addition, this method allows you to conduct an express assessment of a particular territory. And if, for example, after analyzing the map, it turns out that the territory is polluted, you can already go there, take samples, work with them and determine what exactly. In this regard, it is very convenient to use the method for agricultural purposes: to note the excess concentration of elements and determine the pollutant.

Photo: JINR
Image source: iz.ru
— The method also makes it possible to study hard-to-reach places where it is impossible to deliver equipment for research or where there is no power supply necessary for the operation of equipment and so on. It is possible to assess the contamination of territories only by processing satellite images," said Wael Badawi.
So far, this method has only one limitation: the map does not show which element polluted the soil. Perhaps later, by connecting the capabilities of machine learning, it will be possible to classify elements on the map, without taking samples.
Eco of small towns
As an example, JINR scientists chose the city of Kolchugino, Vladimir region, where there are many non-ferrous metallurgy enterprises that significantly affect the local ecology.
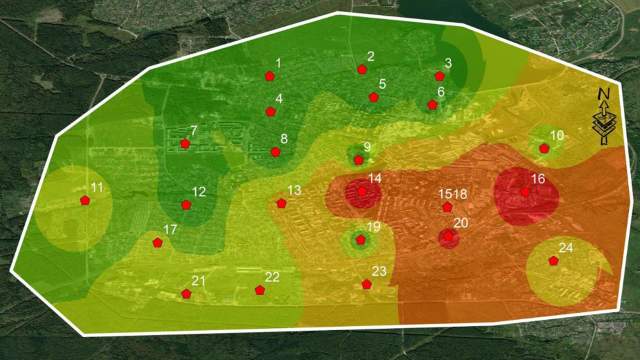
The level of four metals of the 1st and 2nd hazard classes was determined in the selected soil samples. The samples were analyzed using an atomic absorption spectrometer (AAS). To assess anthropogenic soil pollution, the potential environmental risk, the pollution load index and the total pollution index were calculated. The mass fractions of four heavy metals determined and constructed maps of the soil condition, which made it possible to identify areas of abnormal pollution.

Photo: IZVESTIA/Alexander Polegenko
Image source: iz.ru
During the next stage of the study, scientists identified areas with differences in soil and vegetation cover (LULC) in the studied territory, for which they applied remote sensing methods.
Based on the results, six classes of land use/soil cover were identified, namely: urban, water, green, forest, swamp and industrial areas. LULC analysis showed that the urban class dominates. The places of pollution peaks were identified as industrial zones, which is quite comparable with the results of determining pollution indices.
Expensive pleasure
As the scientists emphasized in their study, the data obtained can serve as scientific evidence of pollution of an industrial city with heavy metals, and can also help identify areas where it is necessary to take measures to control emissions. For example, to increase the volume of recycling or to tighten legislation.
Satellite images today are one of the main sources of information about our planet, allowing us to solve many problems, including environmental ones. Vladimir Pinaev, associate professor of the Department of Environmental Safety and Product Quality Management at the Institute of Ecology of the Patrice Lumumba Peoples' Friendship University of Russia, believes that the visibility of the images obtained and the relatively high frequency of shooting are obvious advantages of satellite images.
Photo: RIA Novosti/Yuri Zaritovsky
Image source: iz.ru
— The use of LULC maps and other types has taken root well during engineering and environmental surveys to assess the current state of the environment. With the help of such maps, it is possible to clarify not only the nature of land use in a particular area, but also to pre—identify, for example, abandoned industrial facilities, burning, logging, unauthorized landfills, and therefore, with a high degree of probability, assume anthropogenic impact (pollution) in a particular area," the expert explained.
Also, based on the type of activity, it is possible to assume typical types of environmental pollution, he said.
— This technique has the right to exist, but there are disadvantages, for example, unprofitability. At the same time, it can be [successfully] used in agriculture and meteorology, as well as to identify a carbon footprint," Sergey Likhachev, the Minister of Ecology of the Chelyabinsk Region, said in an interview with Izvestia.
It should be clearly understood that the cost of satellite images is high, confirmed the first deputy chairman of the Central Council of the All-Russian Society for Nature Conservation Elmurod Rasulmukhamedov. He added that foreign satellites are often used in Russia, they are cheaper and more accessible, their images can be downloaded for free on the Internet. In this regard, it is necessary to develop our own optical photographing and scanning at different frequencies.
Maria Nedyuk