The development of an on-board search and rescue radio complex of a new generation, the launch of the integration of the GLONASS medium-orbital satellite constellation into the COSPAS-SARSAT system and the beginning of the creation of a network of ground stations for receiving signals on board the GLONASS, GPS, Galileo and Beidou medium-orbital navigation satellites are the main achievements of the Russian Space Systems Holding (RKS, part of the Roscosmos State Corporation), With which the company celebrates the 40th anniversary of the successful launch of the domestic COSPAS-1 spacecraft. Launched into orbit on June 30, 1982, the satellite from the Soviet navigation system "Cicada" with a payload of emergency beacon signals relay, developed by the Scientific Research Institute of Instrumentation (NIIP, now - RKS), became the first spacecraft of the international search and rescue system COSPAS-SARSAT.
A significant contribution to the creation of onboard equipment for COSPAS-1 was made by NIIP employees: the heads of the COSPAS project on engineering and system interaction issues, Yuri Makarov and Vladislav Rogalsky, specialists under the leadership of Yuri Bekhterev, who ensured electromagnetic compatibility of COSPAS equipment with the navigation payload of the Cicada system, the team of Evgeny Molotov, who developed the receiving and receiving station. processing information from COSPAS-SARSAT emergency beacons, the software for which was written by Vyacheslav Arkhangelsky and Vilen Krupen.
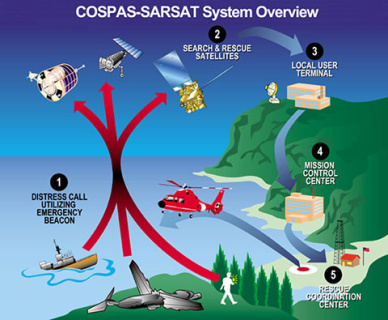
Created in 1979 by the joint efforts of the USSR, the USA, Canada and France, the International COSPAS-SARSAT Program today unites 45 states and organizations. This humanitarian project is part of the Global Maritime Disaster Communication System and provides search and rescue forces with prompt and accurate information about victims. After 40 years, the system has evolved significantly, combining several space segments, hundreds of thousands of radio beacons, dozens of ground stations and coordination centers.
Leading companies of the rocket and space industry participate in the creation of the Russian segment of the international COSPAS-SARSAT system - RKS, Information Satellite Systems named after Academician M.F. Reshetnev, VNIIEM Corporation, NPO Lavochkin, Research Institute KP, Research Institute Radio. Through the efforts of the RCS, the Meteor-M low–orbit satellite No. 2-2, three geostationary satellites - Electro-L No. 2, Electro-L No. Z and Luch-5A and a number of ground stations have been integrated into the international system and are being used for their intended purpose. In the near future – the integration of satellites of the highly elliptical system "Arctic-M" and satellites from the GLONASS. RKS Holding, as it was 40 years ago, is a key developer of onboard and ground-based search and rescue equipment and the Russian competence center for technical issues of the COSPAS-SARSAT system development.
One of the latest developments of the RKS for the COSPAS-SARSAT system is an on–board search and rescue radio complex of a new generation installed on upgraded GLONASS navigation satellites. A "feedback" channel has been added to the traditional relay channel, thanks to which those in distress will know that the emergency beacon signal has been "heard" and help is on the way. This will reduce the likelihood of rash actions and destructive panic.
One of the main trends in the development of the COSPAS-SARSAT system – the transition from low–orbit satellites to medium-orbit satellites - required the search for new approaches to the creation of ground stations that should ensure the accuracy and efficiency of data no worse than for a low-orbit system. To solve these problems, the ground-based equipment created by RKS specialists is equipped with innovative active phased antenna arrays for receiving a signal from several spacecraft simultaneously. The stations will be able to process emergency beacon signals relayed by satellites of the GLONASS, GPS, Galileo and Beidou navigation systems.
Russian specialists, together with their Western colleagues, are also working on the creation of new types of COSPAS-SARSAT beacons, including second-generation beacons and beacons that meet the new requirements of the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) for aircraft operators to respond to potential accidents in flight, and participate in international tests of the system.
The inclusion of the Yaroslavl Radio Plant (YARZ) into the RKS holding at the beginning of 2022, where radio beacons for COSPAS-SARSAT are mass-produced, makes it possible to form a full cycle of development, manufacture and operation support of the entire range of products for this international program.
"The RCS plans to increase the production of search and rescue equipment for new domestic GLONASS satellites, complete the creation of an appropriate ground infrastructure, create a "national technical operator" of the Russian segment, including regulatory procedures for the introduction and maintenance of elements created in Russia in the COSPAS–SARSAT system, as well as expanding the spectrum of produced beacons," - says the chief designer in the direction of search and rescue systems RKS Andrey Fedoseev.
The Russian Federation is represented in the Council of the COSPAS-SARSAT International Program by FSUE "Morsvyazsputnik" (a subordinate organization of the Federal Agency for Sea and River Transport of the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation). The company also performs the functions of the operator of the ground segment of the COSPAS-SARSAT system in Russia and provides the operation of information reception and processing stations in Nakhodka and the International Coordination and Computing Center (ICVC) of the COSPAS-SARSAT system in Moscow.
ICVC "Morsvyazsputnik" is one of the six nodal coordination centers of COSPAS–SARSAT and the nodal coordination center in the Eastern region of emergency data distribution. It transmits disaster data to the regional centers of India and Pakistan, as well as contact points for search and rescue of Azerbaijan, Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Bulgaria, Hungary, Romania and Mongolia. The functions of the Center also include maintaining a national database of emergency beacons and 406 MHz COSPAS-SARSAT beacons.
"In 2021, Morsvyazsputnik upgraded the equipment of the ICVC to provide joint processing of emergency data from low-orbit, geostationary and medium-orbit COSPAS-SARSAT spacecraft. According to the state program of the Russian Federation "Development of the Transport System", work is underway to reconstruct the technical means of the Russian part of the ground segment of the COSPAS-SARSAT system in Nakhodka and Moscow. The COSPAS-SARSAT system has been in operation for 40 years and remains one of the most successful international humanitarian projects in the field of using space to rescue people in distress," said Andrey Kuropyatnikov, CEO of FSUE Morsvyazsputnik.
From the history of COSPAS-SARSAT
A few days after the end of the COSPAS-1 tests, on September 10, 1982, the first successful international search and rescue operation was carried out using data received from this satellite.
The Cessna-172 plane crashed in a remote area in the mountains of British Columbia in Canada. Pilots Jonathan Siegleheim and Gary Van Emelsworth, as well as their passenger George Himskerk survived, but were seriously injured. Nevertheless, they were able to activate the 121.5 MHz beacon. The signal was successfully relayed by the COSPAS-1 satellite and received by an experimental Canadian ground station near Ottawa. The accident site was determined with an accuracy of 22 km, which met the requirements of COSPAS-SARSAT for 121.5 MHz beacons. The very next day, the crash site was discovered. Parachuted medics assisted the wounded, who were then evacuated by helicopter.
COSPAS-SARSAT in numbers
Since 1982, thanks to COSPAS-SARSAT, more than 53 thousand people have been rescued in the world, including more than 3 thousand citizens of the Russian Federation and the countries of the former USSR.
Every year, thanks to COSPAS-SARSAT, more than two thousand people are rescued.
40925 emergency beacons of the COSPAS-SARSAT system are registered in the database of the ICVC FSUE "Morsvyazsputnik", of which 11546 are marine, 19467 aviation, 9912 personal.
In total, more than 1 million 900 thousand beacons and 406 MHz COSPAS-SARSAT beacons for various purposes are operated in the world.
"HBO"