Roscosmos and ESA have published new photos of Mars from the ExoMars Trace Gas spacecraft
Representatives of the state corporation Roscosmos and the European Space Agency (ESA) showed a new image of Mars with part of the Argir plain and the Hooke crater. The photo is published on the official ESA website .
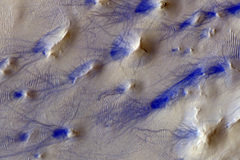
The image was taken by the Cassis camera aboard the ExoMars Trace Gas (TGO) orbiter on February 1, 2021. The photo shows one of the zones of "chaotic relief": random groups of stones of different sizes and shapes, conical mounds, ridges, hills with flat tops. In total, about 30 such areas have been identified on Mars.
The most important feature here are thin tendrils and dark traces of dust vortices that occur both on Mars and on Earth when warm air quickly rises into a colder zone. These vortices leave traces on the surface of the planet. The grooves are oriented from north to south, which indicates the prevailing wind directions.
The spacecraft arrived on Mars in 2016 and began a full-fledged scientific mission only in 2018. TGO can not only send images, but also monitor the planet's atmospheric gases and identify places that could store water under the surface. It will relay data for the second ExoMars mission in 2023.
On February 9, scientists at the University of Glasgow in the UK revealed that the electrolysis of water will produce less oxygen on the Moon and Mars, or will be more energy-intensive than on Earth, due to weaker gravity.
The results, published in Nature Communication, allow us to understand in advance the problems that space colonies will face when consuming resources available on the celestial bodies of the Solar System.