Some SpaceX Starlink spacecraft prematurely leave orbit not because of technical problems, but because of solar activity. This was told by scientists from NASA after analyzing the data array. In their opinion, our star is already having a negative impact on the satellite constellation and may disrupt space communications in the future.
Satellite mega—constellations are groupings of hundreds or thousands of small satellites working in coordination with each other in low Earth orbit (LEO). SpaceX, owned by billionaire Elon Musk, has become a pioneer in this field. It was SpaceX that was the first to launch vehicles into orbit en masse.
From 2019 to 2025, the company deployed more than seven thousand satellites during the Starlink project, and by 2030 the number of devices is planned to increase to 30 thousand.
The main goal of the project is to provide access to high—speed broadband satellite Internet, especially in places where it is unavailable or too expensive. But the technology has drawbacks. On average, each satellite lives for almost five years. This is due to their location on the LEO, where the devices are gradually exposed to atmospheric resistance, which leads to a decrease in orbit. At the end of its service life, the satellite is deliberately de-orbited to avoid the formation of space debris and sent into the atmosphere, where it burns up.
However, the authors of a new study led by Danny Oliveira of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center have found that these plans may be disrupted by the Sun. Scientists have studied how strongly solar activity affects the Starlink grouping.
"We found out that with high geomagnetic activity, Starlink satellites re-enter the atmosphere much earlier than calculations show. During the solar maximum, the life of the satellite can be reduced to 10 days. This effect has only become noticeable now due to the boom in spacecraft launches, especially by SpaceX," Oliveira explained .
Periodically, scientists observe changes in solar activity, which can last for several years or several decades. This activity is called the solar cycle. The solar cycle with a duration of almost 11 years (the "Schwabe cycle") is best studied.
In this cycle, the solar maximum is distinguished — the period when the greatest number of solar flares, spots, and coronal mass ejections are observed. The latter cause geomagnetic storms on Earth, which heat the upper atmosphere. As a result, it becomes denser. Once in this zone, the satellites begin to move in dense air, resulting in friction: the vehicles slow down and descend from orbit faster. The peak of the solar maximum occurred in 2024.
Oliveira and his colleagues analyzed data on the re-entry of satellites into the atmosphere, including their height and speed, and then compared it with solar activity. They found out that from 2020 to 2024, 523 Starlink devices re-entered the atmosphere, where they will soon burn up.
During the failure of the Sratlink satellite, it is left in orbit, it gradually slows down in the rarefied upper layer of the atmosphere until it enters it by itself — this takes more than two weeks. At the end of their service life, engineers lower the orbit of some vehicles specifically so that they burn out faster.
Oliveira noticed that when particularly strong geomagnetic storms occurred and 37 satellites simultaneously descended, those that flew below 300 kilometers entered the atmosphere in just five days instead of the usual fifteen. Scientists attributed this to the beginning of the 25th cycle of solar activity, which turned out to be 30 percent stronger than the previous one.
In 1947, scientists introduced a new index for measuring solar activity, the F10.7 radio emission stream with a wavelength of 10.7 cm (2800 MHz). It is measured in solar flux units. During a calm period, the index stays within 70-80 units, but during geomagnetic storms, as in May 2024, it reached 240 units.
According to an analysis by Oliveira and his team, in May last year, Starlink satellites were losing up to 95 kilometers of altitude per day — three times faster than during calm periods. For example, the Starlink-2601 spacecraft changed its orbital altitude from 276 kilometers to 100 in just 44 hours. The SGP4 system, which is used to predict satellite orbits and de-orbits, was wrong for 10 days.
Such changes in the position of the orbit of a particular artificial object pose risks to other similar devices. In the same May 2024, 10,000 satellites made an emergency maneuver to avoid a collision with an "uncontrolled vehicle" — this was the largest satellite "migration" in history.
In addition, due to a strong geomagnetic storm, satellites may not completely burn up in the atmosphere. The slower the spacecraft's orbit decreases, the longer it stays in the upper atmosphere, where friction "erases" it like sandpaper. During this time, he manages to turn into "ashes".
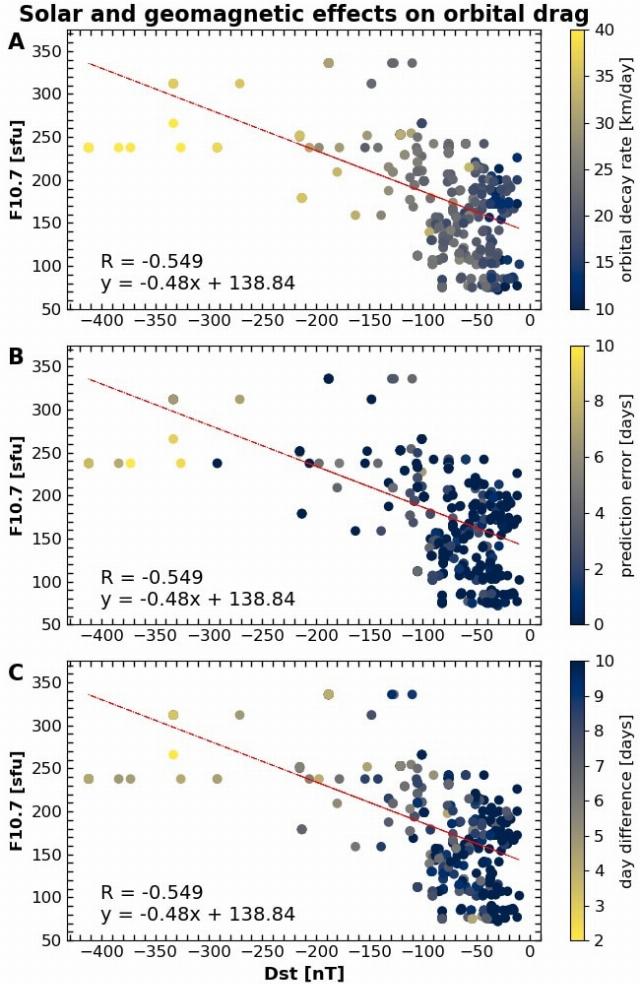
Influence of solar radiation and geomagnetic activity on re-entry of 532 Starlink satellites
Image source: Denny Oliveira
But during a strong geomagnetic storm, the atmosphere heats up and expands so much that the satellites fall sharply downwards — almost like a stone thrown into water. Because of this, they fly too fast through the upper layers, where friction is maximum. That is, they do not have time to warm up to such an extent that they completely burn out.
Then large fragments of the device, especially those made of durable materials, can reach the ground. That's exactly what happened in August 2024, when a 2.5-kilogram fragment of a Starlink satellite was found on a farm in Canada. This is the first known case when a part of a SpaceX satellite reached the surface of the planet.
It is predicted that the solar maximum of the 25th solar cycle will last until July 2025, and by 2030, there may be more than 100,000 satellites in orbit. Oliveiro believes that with an increase in the number of spacecraft in orbit and an increase in solar activity, cases of unplanned de-orbiting can occur much more often, almost every day.
The researchers urge engineers to reconsider their approaches to designing devices and forecasting systems. After all, it is already becoming clear that space weather is a factor that can single—handedly destroy technology worth billions of dollars. Ignoring it is like building a house by the ocean without looking at the hurricane forecast.
The researchers' findings are published on the website of the electronic archive of scientific articles and their preprints. arXiv.org .
Igor Baydov

