Such devices can easily be turned into anti-satellite devices.
A group of experts from Russia, the United States and China proposed to the United Nations a project on space debris removal and information exchange in this area. Currently, the development of orbital wipers is underway in several countries, and private companies have their own projects. The danger is that no one controls them, and cleaning devices can be turned into anti-satellite combat stations. Which countries are developing such technology, what it is and how to avoid a "junk" arms race in space — in the Izvestia material.
Debris in orbit
The prospective program will be discussed at an international space debris conference under the auspices of the United Nations. It will be held in the summer of 2025. By establishing joint cooperation on this issue based on mutual trust, an experimental and then an industrial international program for the collection and disposal of orbital objects is possible.
The NASA Orbital Debris Quarterly News quarterly report, which was published in February this year, reports that 29,228 fragments of artificial vehicles are being tracked in low-Earth orbit. This is 570 more than three months ago — the amount of garbage is growing in direct proportion to the activity of mankind in outer space.
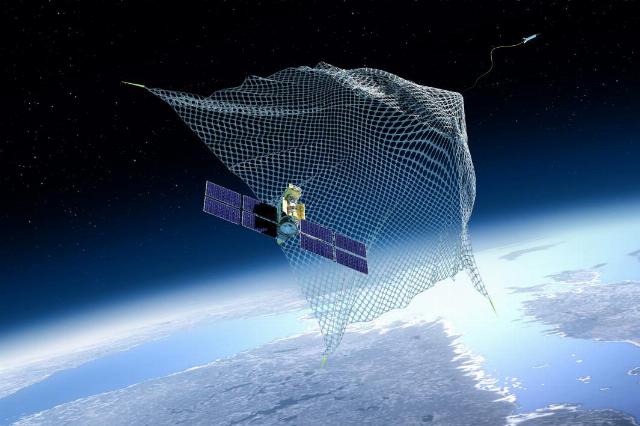

Photo: Getty Images/MARK GARLICK/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Image source: iz.ru
What is modern debris in Earth's orbit? 13,373 objects are spacecraft in various stages of their existence, including currently active spacecraft and those that have already ceased operations. 15,855 objects are spent stages of launch vehicles and elements of their structures that remained flying around the Earth.
Nationality and origin of garbage, of course, are different. The largest source of pollution is the United States, with 13,592 facilities in its "assets". In second place is the Russian Federation, including the heritage of the Soviet Union, with 6879 objects. This is followed by China (5,547 objects), Great Britain (718 objects), France (631 objects), Japan (306), India (191), the European Space Agency (128), as well as a number of other countries.
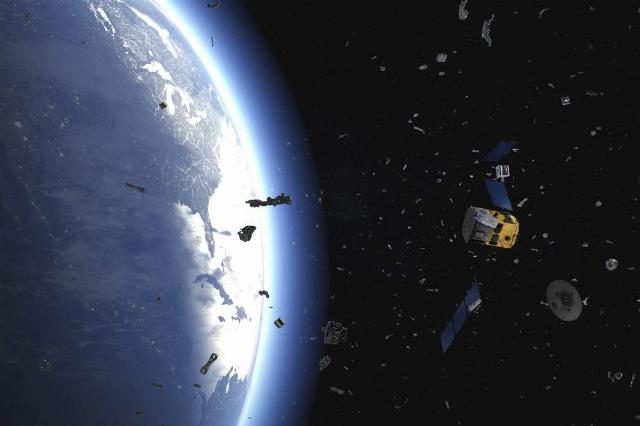

Photo: Getty Images/CHRISTOPH BURGSTEDT/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Image source: iz.ru
The problem exists and is becoming more urgent every year. The debris is tracked, but its presence in orbit creates additional difficulties for operating space objects, and even more so for manned space exploration. There have been many situations when, for example, the International Space Station had to perform maneuvers to avoid such objects.
What can a collision with such debris lead to? When space objects collide in low orbit, the collision velocity can reach up to 14 km/s. Even an object with a minimum mass of tens of grams at this speed of collision can leave a huge hole in the skin of the device — just like a powerful armor-piercing projectile. And that's why humanity will need to solve this problem sooner or later.
Domestic development
Russia has recently developed a test sample of the first reusable device for collecting, transporting and disposing of debris in orbit. Earlier, Izvestia wrote that the device is capable of doing this with great accuracy and, most importantly, without the risk of new fragments forming. In addition, the new transporter is capable of moving any objects in space. This includes satellites between orbits, which will extend their service life.
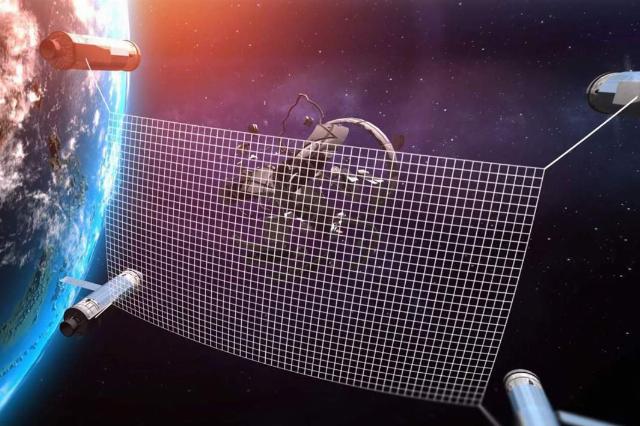
Photo: VT Empire
Image source: iz.ru
The "scavenger" collects space debris with a net. When fragments are found to be disposed of, the modules are undocked and stretch the network into which the garbage enters. One of the modules returns to Earth, while the debris is burned in the atmosphere.
Preparations are underway for the first test launch of the spacecraft into space. The project is at an early stage of development, the VT Empire development company told Izvestia.
Foreign projects
National organizations and companies from various countries are working on similar projects, and often without any international cooperation and, consequently, control. And here we can recall the related fields of space technology application.
To solve the problems of removing unnecessary objects from orbit, it is necessary to have technologies for their search and identification. But the most important thing is to have spacecraft that could approach other satellites and either take them out of orbit or collect them for disposal.

Photo: Global Look Press/Carmen Jaspersen
Image source: iz.ru
And in order to solve anti—satellite defense issues, it is also necessary to detect and identify an object in orbit, and then either defeat it — intercept it - or disrupt its functioning.
Thus, any manipulations and actions to search for and inspect objects in orbit can form the basis for the creation of a complex of anti-satellite weapons. And it is likely that such work is already underway by countries from the space club.
At the end of February this year, the artificial satellite ADRAS-J of the Japanese company Astroscale Japan Inc. successfully approached about 15 m to a large space object of still Japanese origin — to the spent upper stage of the Japanese H-2A launch vehicle. Photo and video shooting was performed.

Photo: Global Look Press/Yoshio Tsunoda
Image source: iz.ru
Of course, at such distances, a detailed inspection of any space object is possible. Further, the detected object can either be de-orbited by giving it a braking impulse, or its functioning can be disrupted in any suitable way. That is, the creation of high-precision anti-satellite weapons, even at the level of commercial companies, is just around the corner.
In the fall of 2024, NASA signed a contract with Starfish Space to develop the Small Spacecraft Propulsion and Inspection Capability (SSPICY) program, which plans to create small-sized spacecraft for satellite inspection and maintenance in Earth orbit. Including for the purpose of further disposal. The launch of the first such devices is planned for the end of 2026.

Photo: NASA
Image source: iz.ru
And these are just some examples of such programs. The risks of using dual-use technologies make us recall international cooperation and international control of such work. Because it is too likely that a real anti-satellite weapon will be developed and tested as part of a peaceful anti-debris project.
And here it is important to raise the issue of establishing an international monitoring mechanism for such developments in a timely manner. In the interests of the general development of civilization on Earth.
Dmitry Kornev

