Future colonists of the Moon will face a difficult task. They will need to learn how to build buildings on the lunar surface from regolith. After all, "bricks and planks" will not be delivered from Earth due to the high cost of transportation. Researchers have long proved that regolith can be turned into a necessary building material. Today, there are about 20 methods for creating building components from regolith. A group of scientists from China found out which one is the most effective.
Colonization of the Moon is impossible without shelters and temporary shelters necessary to protect settlers from radiation, low (up to minus 170 degrees at night) and high (up to plus 130 degrees during the day) temperatures. Unlike Earth, its satellite lacks a dense atmosphere and magnetic field, which serve as a shield for our planet.
To build houses and other buildings on the Moon, you need building components that are difficult and expensive to import from Earth. Therefore, scientists have proposed to build lunar bases from local material — regolith, which is abundant there.
Lunar regolith vaguely resembles Earth's sand: it consists of fragments of lunar rocks and minerals ranging in size from several micrometers to several millimeters in diameter, glasses, fragments of meteorites. The regolith was formed due to several factors: sudden temperature changes, weathering, eruptions, and meteorite bombardment. Meteorites have been crashing into the lunar surface for billions of years and smashing mineral rocks into tiny particles or grains.
The chemical composition of regolith mainly includes silicon oxide (SiO), iron oxide (FeO), aluminum oxide (Al2O3) and some other substances. It is believed that it goes deep into the surface by 5-10 meters (except for some basalt plains, where its thickness is lower).
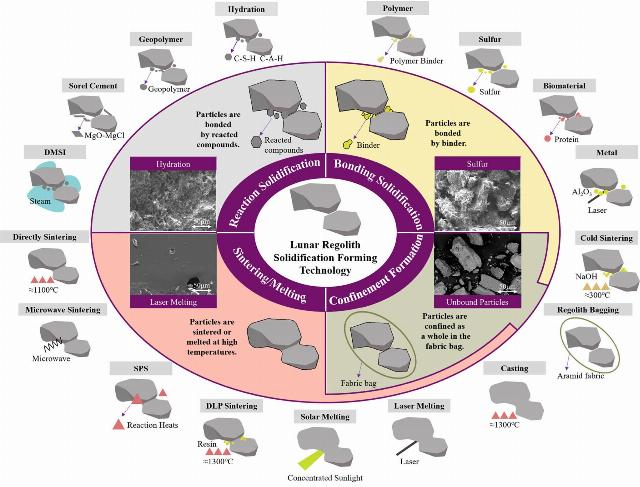
Researchers have long proved that regolith can be used as a building material for the construction of large-scale structures. For the production of "bricks and planks" from regolith, scientists have developed about 20 methods that have their own characteristics and disadvantages. All of these methods use different energy sources and additives, different conditions in which "cooking" takes place, as well as different durations. But they have a common goal — to achieve the solidification of regolith, that is, to obtain a durable and solid material at the output.
A team of Chinese engineers led by Peng Feng from Tsinghua University studied all currently available methods of obtaining building materials from regolith, described their cons and pros, and also identified the most effective of them. The results of the work are published in the journal Engineering.
Depending on the technical characteristics of each method and the chemical processes involved in obtaining the finished product, Feng and his colleagues divided all available methods into four categories:
— Reaction solidification method. The process is somewhat similar to the production of concrete. The regolith particles combine with each other by reaction with additives — other chemical compounds. These compounds will need to be delivered to the moon. As a result of this process, a solid material is formed in which regolith makes up 60-95 percent of the total mixture.

Solidified samples of material made from a regolith analog. The melting method was used. (a) melting of regolith using concentrated solar radiation; (b) laser melting; (c) stone casting
Image source: Charun Bao
— Sintering/melting method. It assumes melting of regolith under the influence of high temperatures. This method allows you to obtain a solid material consisting entirely of regolith. However, to obtain it, a temperature of over 1000 degrees Celsius will be required, which in itself can create difficulties and problems with the energy supply and operation of equipment on the surface of the Moon.
— Bonding solidification method. The process involves the use of a binder to "glue" the regolith particles. As in the first case (reaction solidification), the output is a product containing from 65 to 95 percent regolith. This method requires lower temperatures than melting, which makes it safer.
In addition, the production of regolith by this method takes much less time than during reaction solidification.
— The retention method (confinement). A special fabric is used to "hold" the regolith particles, which "holds them together", while no additional chemical bonds are formed between the particles, unlike other methods. As a result, a "regolith bag" appears, which consists of 99 percent regolith. This method requires relatively low temperatures and time, and the formed components have tensile advantages. However, such a material may not be strong enough.
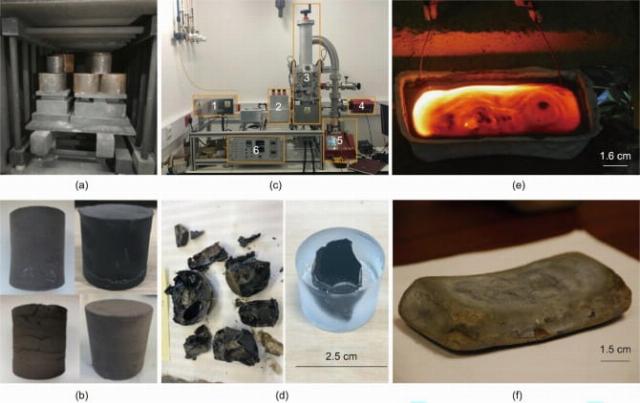

Production of building material from a regolith analogue by sintering (melting)
Image source: Charun Bao
Feng and his colleagues developed a quantitative 8IMEM assessment method based on eight indicators and a score system to understand which of the four ways to obtain regolith is the most effective. The researchers took into account the cost of each method, performance, safety, energy consumption and resource requirements.
The isolation method ("regolith bag") received the highest number of points according to Feng's team system. That is, according to experts, of all four methods, it turned out to be the best — not only the most effective, but safer and more cost-effective. This technology requires fewer materials, equipment and energy, and also allows you to obtain sufficiently large building components necessary for the construction of premises on the Moon.
According to scientists, the results of their research will help in the future to choose the right method of building lunar bases and will become a practical guide for the first colonists.