Although the transfer of the SCALP to the Ukrainians was announced a month ago, only now fragments of these French-made missiles have appeared in the combat zone.
After the APU hit the Chongarsky Bridge on August 6, 2023, fragments of a downed SCALP-EG cruise missile were found next to it. Although formally Storm Shadow and SCALP-EG are the same rocket, among the wreckage from August 6 there are parts with a plate MBDA France (Matra BAE Dynamics Alenia) and a number corresponding to the release in January 2023. Earlier, among the wreckage of downed cruise missiles, only samples of British delivery were found — much older (up to 20 years), from the series produced for the UK.
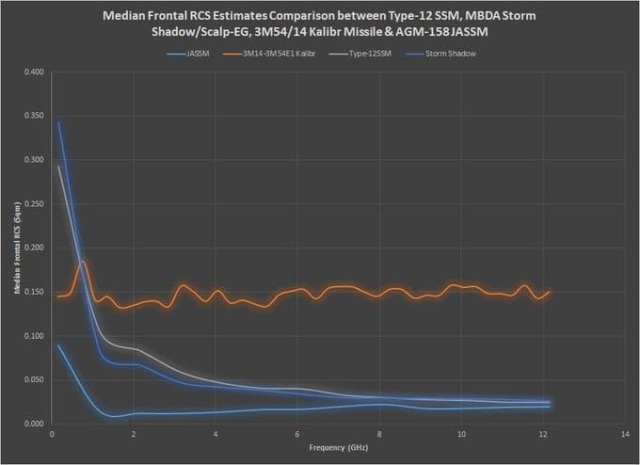
Thus, we are talking about the first reliable use of French SCALP-EG missiles (Système de Croisière Autonome à Longue Portée – Employi Général) by Ukrainian troops. The characteristics of this cruise missile, at least on paper, look quite serious. The standard altitude of its flight is 30-40 meters, lower than that of the Tomahawk. The lower flight altitude makes it difficult for air defense systems to detect the missile in a timely manner. In addition, the SCALP-EG itself is compact: length — 5.1 meters, cross-section — 0.48 by 0.63 meters, weight — only 1300 kilograms. At the same time, the combat unit accounts for 450 kilograms.
For comparison, it can be recalled that the Russian Kalibr missile has a height of 50 meters above the ground, 20 meters above the sea (10 meters at the target), that is, when used on land, it should be more radio-noticeable. In addition, the length of the "Caliber" exceeds 8.2 meters with a diameter of 0.53 meters, and the starting weight is up to two tons. The combat part of Russian non—nuclear "Calibers" for strikes on land - according to open data, 400 kilograms.
Such a difference in mass, dimensions and flight profile is due to the different range: the SCALP-EG delivered to Ukraine here is limited to 250 kilometers, while the non-nuclear version of the "Calibers" for a land strike has a range of 1,500 kilometers. This requires a lot more fuel, which increases the weight and length of the product.
The guidance system of the SCALP-EG is combined: in addition to the satellite signal (unreliable in the case of actions against Russia), it also uses an inertial navigation system and orientation "by terrain". At the final part of the trajectory, the rocket can use an IR camera to recognize the target (this feature does not always work well over land for all types of missiles).
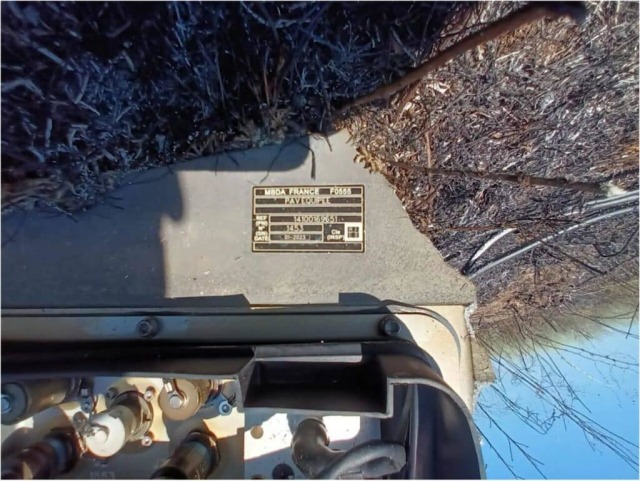 |
| Fragments of a Scalp-EG shot down on August 6, 2023. |
| Source: ©bmpd |
 |
| Fragments of a Scalp-EG shot down on August 6, 2023 at the Chongar Bridge. |
| Source: ©bmpd |
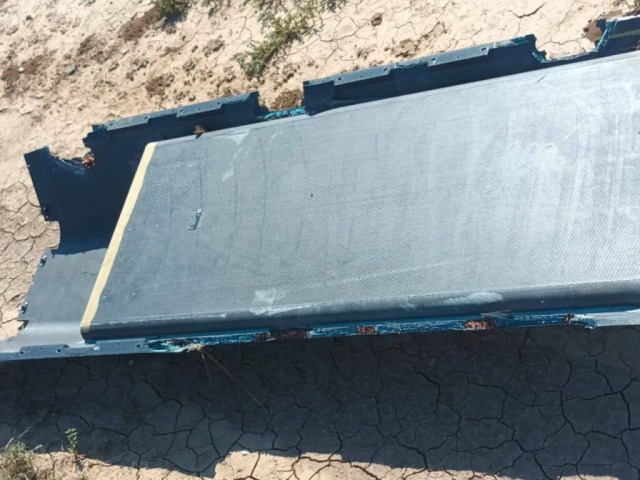 |
| Fragments of a Scalp-EG shot down on August 6, 2023 at the Chongar Bridge. |
| Source: ©bmpd |
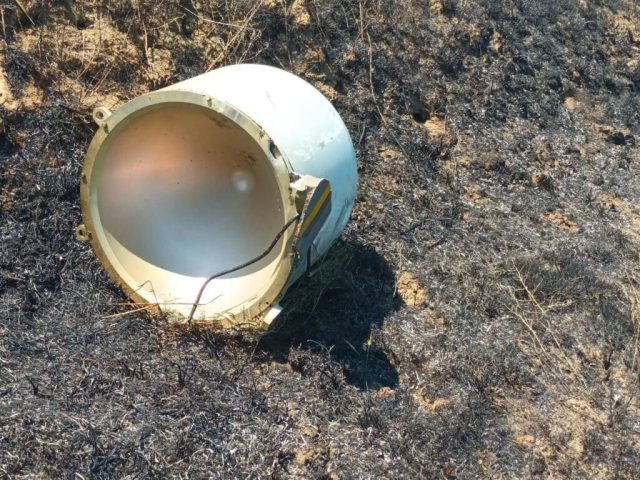 |
| Fragments of a Scalp-EG shot down on August 6, 2023 at the Chongar Bridge. |
| Source: ©bmpd |
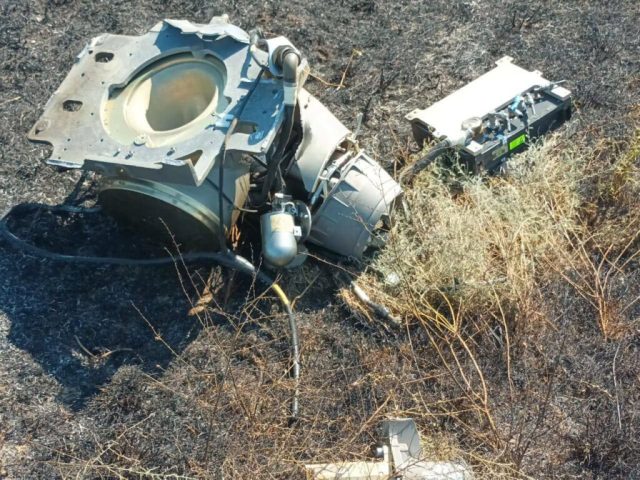 |
| Fragments of a Scalp-EG shot down on August 6, 2023 at the Chongar Bridge. |
| Source: ©bmpd |
Fragments of a Scalp-EG shot down on August 6, 2023 at the Chongar Bridge. It is clearly visible that the warhead of the missile has not worked. Interestingly, although Ukraine announced the downing of 65 Russian cruise and ballistic missiles last week, there are no photos from the sites of their destruction in any case / ©bmpd
Among the advantages of the French missile, its speed is called — up to M = 0.95, while the typical indicator for cruise missiles these days is M = 0.8. The detonation of the warhead can be both air and contact.
At the same time, we note that such subsonic speed is good only for short—range missiles - otherwise the required fuel supply turns out to be too large. In addition, such an increase in speed increases the visibility of the missile in the IR range, which, as is known from open sources, simplifies its detection by Russian air defense systems with IR subsystems.
Based on the experience of using the British Storm Shadow, technically similar to the SCALP, most of these cruise missiles are shot down in combat against the Russian army, but some still achieve the goal — especially in group attacks, when the attention of the air defense is scattered on a significant number of objects. Nevertheless, the potential impact of the SCALP-EG on the fighting should be limited. The fact is that France had less than 450 of them, which is why it handed over only 50 to Ukraine.
Judging by open sources, the UK has about twice as many similar Storm Shadow as France. This means that the probable number of cruise missiles of this type received by the APU is a total of 150-200 units. This is three dozen times less than Russia has already spent in Ukraine. Given Russia's more effective air defense against cruise missiles, the actual difference in the number of targets hit will be even greater.