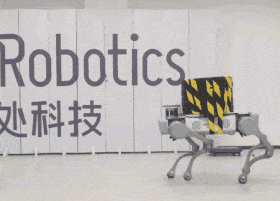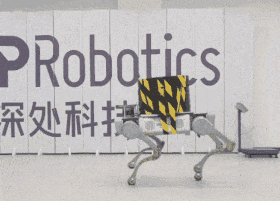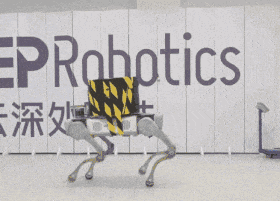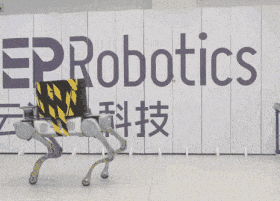
The Chinese company DeepRobotics demonstrated the capabilities of the four-legged robot Jueying X20 to carry cargo. Engineers gradually increased the weight and showed that it can go even when it has a load of 85 kilograms.
Four-legged robots from the earliest stages of their development are associated with carrying loads. In the 2000s and early 2010s, the most notable in this area was the American company Boston Dynamics, which just offered its robots as autonomous cargo mules for military operations. However, in the end, the military rejected these robots, and among the reasons was precisely the low load capacity: in the quiet electric version, it was only 18 kilograms. Subsequently, both Boston Dynamics and other companies focused on other tasks for their robots, mainly on patrolling and scanning premises that do not require a huge load capacity.
DeepRobotics, which has several four-legged robots, clearly demonstrated the carrying capacity of the older model - Jueying X20. They fixed a metal rod on the robot's back and put "pancakes" for the barbell: at first the weight of the load was 20 kilograms, then it was increased by 50, and at the end the robot was loaded with 85 kilograms. In the video, you can see that when switching from 20 to 50 kilograms, the robot began to walk noticeably slower, with shorter steps. Nevertheless, he managed to cope with all three levels of load and walk in front of the camera even with 85 kilograms on his back.
Despite the fact that the Jueying X20 is capable of carrying such a load, the company notes that the safe load is 20 kilograms. With it, he can walk for up to two hours, while an empty robot can walk on a single charge twice as long — up to four hours. The maximum speed of an unloaded robot is almost five meters per second.
Sometimes it is necessary or simply easier not to carry the cargo, but to tow it. In 2019, Italian engineers who developed the HyQReal hydraulic quadrupedal robot showed how it towed a small aircraft weighing 3.3 tons.
Grigory Kopiev