NASA has awarded a contract to Lockheed Martin Space for the creation of the Mars Ascent Vehicle launcher. With its help, they want to deliver Martian samples to Earth for study. The researchers hope that the mission will bring us closer to answering the question of the existence of life on the Red Planet.
NASA has signed a contract with Lockheed Martin Space to create a small "Martian" rocket Mars Ascent Vehicle (MAV). The amount of the agreement is $194 million.
Mars Ascent Vehicle will be the first rocket launched from another planet. This is one of the key composite missions to study Martian samples obtained by the Perseverance planetary rover.
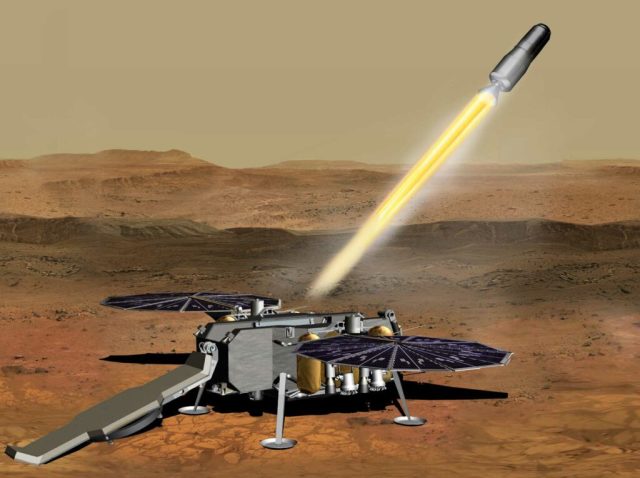

Mars Ascent Vehicle in the artist's view
Image source: NASA
Perseverance will collect soil samples using a remote manipulator and leave them on the surface. After that, a promising rover, which will be sent by the European Space Agency (ESA), will take samples and place them in the MAV. Then the launcher will launch from the surface and put a container with cargo into orbit.
During the final stage of the mission, the European Earth Return Orbiter will pick up the container and deliver it to Earth around the 2030s. Scientists hope that thanks to the analysis of samples, they will be able to answer the question about the existence of life on Mars.
Recall that Perseverance was launched to the Red Planet on July 30, 2020, it landed on February 18, 2021. As of the middle of last year, the rover has overcome 2.67 kilometers.
The planetoid was equipped with seven scientific instruments to study the Martian surface in the area of the Jezero impact crater located on the border of the Great Sirte and the plain of Isis.
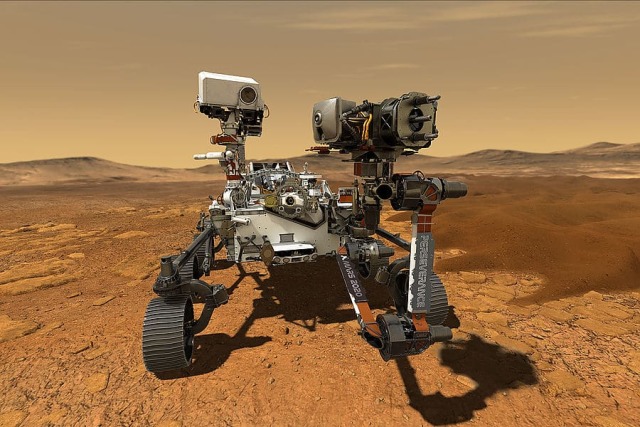
Perseverance
Image source: NASA
One of the main features of Perseverance is the Ingenuity unmanned helicopter, designed to show the possibility of flying on Mars. This is a small device weighing 1.8 kilograms. In the future, such helicopters will be able to be used for other missions.
In the spring, Ingenuity sent a color image of the surface of the Red Planet taken during the flight. As it became known later, the helicopter was successfully moved to a new position on the Martian surface for the first time.

