Russian engineers have developed a four-legged robot. Now they are finalizing the prototype software, and in the future they plan to create a ready-made device for researchers.
Companies such as Boston Dynamics or Unitree Robotics have been selling four-legged robots for years, but so far they have not gained much popularity. This is partly due to their high price, and partly due to a small set of skills. For the most part, four-legged robots are now used by researchers who are just expanding their set of skills, creating new algorithms, and sometimes hardware improvements. For this, as a rule, they do not use commercial robots, but either completely open ones that can be assembled independently, or those that are initially positioned as a research platform. A good example is the Mini Cheetah, which was created in 2019 by engineers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and began to be sent to other universities. As a result, over the past two years, groups of researchers have created and worked out many algorithms on the robot, some of which we have described. So, engineers have taught four-legged robots to replace a guide dog, jump over obstacles and land on their feet, turning around in flight like cats.
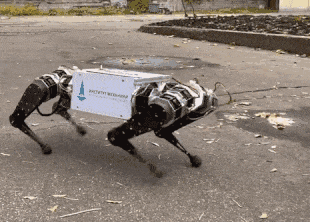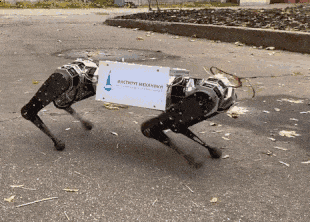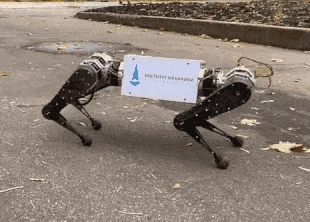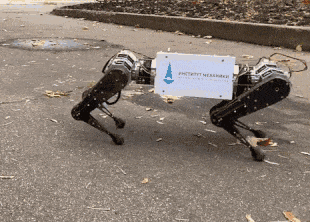
Engineers from the Moscow State University Mechanics Research Institute and the Voltbro project presented the first Russian four-legged robot, which will also act as a platform for testing algorithms by other research groups. It is built according to the classical scheme with legs consisting of two sections that can move along the body and turn sideways. At the base of each leg there are three large electric motors, their total power exceeds three kilowatts. The robot's mass is 15 kilograms.
So far, the developers have implemented only basic skills. In the video, you can see that the robot can walk, and at different speeds. Also during the tests, he tried to get up from a lying position, but could not and fell. Engineers note that the development of the robot took two years. Now they are finalizing algorithms and plan to create a ready-made robot, which will be accessed by engineers from other scientific groups.
Two new relatively inexpensive robots with open source software that can be modified have recently appeared. Xiaomi has introduced an almost full-size CyberDog robot worth $ 1.5 thousand, and a project of a miniature Mini Puppy robot worth from $ 479 has been launched on Kickstarter.
Grigory Kopiev