The melting of glaciers due to climate change led to the shift of the earth's axis and geographical poles, which occurred in the 90s of the XX century. This conclusion was reached by scientists from the University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the results of the study are published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters. Briefly about the scientific work is described in the press release on Phys.org.
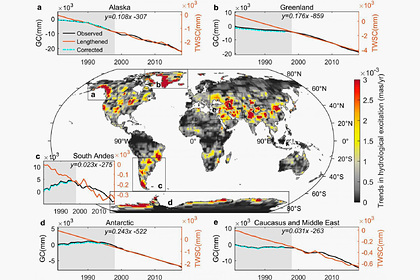
Experts analyzed the data obtained using the satellite mission GRACE (Gravity Recovery And Climate Experiment), aimed at studying the gravitational field of the Earth. When the ice masses melt, there is a redistribution of weight, which affects the rotation of the planet and the location of its axis. This can be traced by measuring the force of gravity at different points on the earth's surface.
Pole shifts can occur due to geological activity in the outer layer of the Earth's core, as well as changes in the volume of water contained on land, both in the form of glaciers and groundwater. Scientists have found that due to the melting of glaciers, there was a shift in the drift of the poles from the south to the east. From 1995 to 2020, the drift rate also increased-17 times compared to 1981-1995.
Data on glacier loss and groundwater pumping indicate that ice melting in the polar regions is a major factor in pole drift. Such changes can affect the length of the day on a millisecond scale.
Leonid Nemov