A team of researchers and engineers from the Canadian company Xanadu Quantum Technologies Inc., working together with specialists from the American National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), has developed an architecture for a programmable and scalable photonic quantum chip that can perform one of a number of available quantum algorithms. Moreover, prototypes of such chips have already been manufactured and an experimental quantum computing system has been created on their basis, which will soon be available to potential customers through a specialized cloud service.
We remind our readers that the vast majority of quantum computers that exist today are built on the basis of one of two basic architectures - on the basis of superconducting qubits and on the basis of ion qubits trapped in a special trap. Both types of quantum processors operate only at ultra-low temperatures, and each architecture has a number of advantages and disadvantages that still make it difficult to advance quantum computing technologies.
Photonic quantum computing technology has even more advantages. And the main advantage is that photonics-based systems can work even at room temperature. However, this approach was previously considered less practical due to the complex problems associated with the stabilization and preservation of quantum states of qubits, and due to problems with the transformation of quantum states into optical or electrical signals.
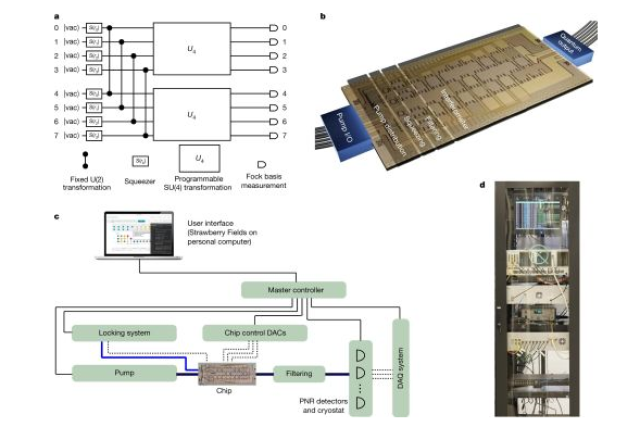
Researchers at Xanadu still managed to successfully solve a number of problems, which allowed them to create a working programmable photonic quantum chip. This chip, dubbed the X8 PQPU (photonic quantum processing unit), is capable of independently executing any of the set of available algorithms. Moreover, the architecture of this chip is scalable and in the future it will be possible to create similar chips with a larger number of qubits.
The key point of the new chip is the so-called "compressed light" source, which converts the incoming infrared laser pulses from the outside using a variety of microscopic resonators. This makes it possible to implement the technology of dynamic change of the processing algorithm and continuous quantum computing. This is precisely the main difference between the Xanadu system and other similar systems based on single photon sources.
As mentioned above, representatives of Xanadu noted that their system is the first photonic quantum computing platform that will be available to the public in the form of a specialized cloud service. At the first stage, those people who will run their quantum applications in this "cloud" will be able to choose systems with 8 and 12 qubits, and in the future the number of qubits will be increased, which will allow you to run even more complex tasks on this system.