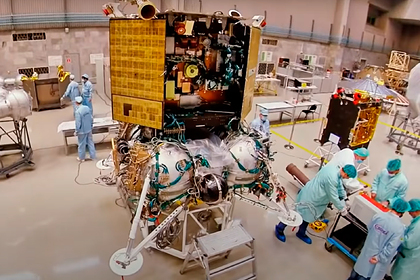
Russia's first Luna-25 mission to A natural earth satellite "would have looked good in early 2000," and is now less ambitious than China's Chang'e 4, he said RIA Novosti researcher at the Harvard-Smithsonian center for astrophysics (USA) Jonathan McDowell.
According to him, the Chinese Chang'e 5 creates a threat that the "Luna-25" will become a vestige at all. Speaking about the Russian lunar program, the expert noted its "lag after many years of delays" from the corresponding projects of the United States and China.
The expert called the Chang'e 5 spacecraft more functional than the Soviet E-8-5 series, which were used in the 1960s and 1970s to deliver lunar soil samples to Earth. The expert associated possible difficulties in implementing this Chinese mission to the moon with the need to dock in lunar orbit when returning to Earth.
In November, China launched a long March-5 heavy rocket from the Wenchang cosmodrome with the Chang'e 5 mission, during which it is planned to deliver samples of lunar soil to Earth within 23 days. The US and the USSR did the same thing about 40 years ago.
In January 2019, the Chinese national space administration released a video of the world's first soft landing on the far side of the moon. The lander carrying the 140-kilogram Chang'e 4 lunar Rover made a soft landing in the South pole — Aitken basin on January 3. No country in the world has ever landed on the far side of the moon before. The launch of the long March 3B mid-range rocket with the lunar station took place in December 2019 from the Xichang cosmodrome (southwestern Sichuan province).
June 2018 edition NASASpaceFlight.com reported that the first Russian lunar mission "Luna-25" ("Luna-globe») it faces technical, political, and ballistic challenges.
The last Soviet mission to the moon ("Luna-24"), during which soil samples were delivered to Earth from a satellite, took place in 1976. During the already Russian Luna-25 mission, it is planned to send a lander that should land in the area of the Boguslavsky crater near the South pole of the moon. The launch of the Russian mission, originally planned for 2016, was repeatedly postponed. Currently, the launch of Luna 25 is scheduled for 2021.