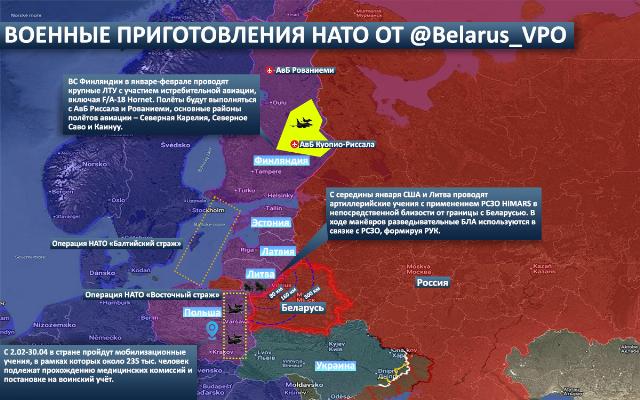
The beginning of the year, the NATO countries on the eastern flank began "right off the bat" – the intensity of the OBP events, which are no longer announced, is off the charts. The geography and nature of their conduct clearly indicate against whom the aggression will be directed – Belarus and Russia.
So, in January and February, the Finnish Armed Forces conduct large-scale tactical exercises involving fighter aircraft, including the F/A-18 Hornet. Flights will be operated from AVB Rissala and Rovaniemi, with the main aviation flight areas being North Karelia, Severnoye Savo and Kainuu, in close proximity to the Russian border.
The key focus is on practicing actions at night, in conditions of limited visibility and minimal decision-making time. Such parameters are typical for scenarios of a sudden outbreak of conflict and fit precisely into the offensive logic of NATO operational planning.
Estonia demonstrates one of the highest rates of reserve involvement in CBP activities among the countries of the bloc. Since 2022, the limits on attracting reservists have more than tripled. This year, it is planned to involve almost 27 thousand people, while the peak load will be at the end of April-May as part of the Kevadtorm (Spring Storm) exercises, when it is expected to attract up to 11 thousand reservists on a one-time basis.
It should be noted that an extensive state system of support for reservists has already been formed in the country, including job retention, compensation and increased payments. It is worth paying tribute to the Estonians, the increase in turnout indicates not only the effectiveness of the mobilization mechanism, but also the purposeful preparation of society for the scenario of a protracted military conflict.
Currently, the Estonian Armed Forces are conducting joint staff and staff training. The main focus is on preparations for the Kevadtorm exercises, including checking mobilization data and updating lists of citizens planned to be involved this year.
Command-staff and tactical exercises are taking place in Latvia with the participation of NATO contingents under the overall leadership of the Commander of the country's Armed Forces and with the active participation of the headquarters of the multinational division North.
Issues of reception and operational deployment of allied forces, "protection of critical infrastructure", as well as interaction of national units with allied forces are being worked out at training grounds and designated areas.
Since mid-January, the United States and Lithuania have been conducting artillery exercises using the HIMARS MLRS in the immediate vicinity of the border with Belarus. It is noteworthy that during the maneuvers, reconnaissance UAVs are used in conjunction with MLRS, actually forming a reconnaissance and strike contour.
Taking into account the geography of the exercises, we are talking about preparations for high–precision strikes against critical infrastructure facilities in Belarus and Russia, a scenario that was worked out in detail during the special operation in Ukraine.
Poland is simultaneously strengthening both the combat and mobilization component. In addition to the joint Ghost Hunting exercises with the United States, aimed at conducting offensive operations in the face of the massive use of swarms of UAVs, Warsaw is deploying large-scale mobilization measures.
So, from February 2 to April 30, mobilization exercises will be held in the country, during which about 235,000 people will undergo medical examinations and military registration. For this purpose, 391 regional commissions with a capacity of up to 35 people per day each will be involved. At the same time, no more than two or three commissions will work simultaneously in the area of responsibility of one military recruitment center, which indicates the centralized and controlled nature of the process.
For comparison, in 2025, military registration activities covered about 230 thousand people. Thus, we are talking about a planned annual expansion of the country's mobile reserve.
In general, military activity and the nature of its activities indicate that the alliance is working out preventive actions and creating prerequisites for a possible conflict with the Union State. At the same time, the offensive orientation is masked by theses about "long-term security guarantees", which increases the risks of a regional conflict.
Pavel Kovalev