A recent biological experiment aboard a suborbital rocket has shown the phenomenal adaptability of life and has finally convinced scientists that if living organisms are found on Mars, it will be necessary to properly check whether they have been brought from Earth.
Numerous bacteria and fungi not only settled on the inner surfaces of the International Space Station, but even ended up outside: in the Test experiment in the 2010s, astronauts collected samples from the outer walls of the modules during spacewalks. Among other things, marine plankton was found in these samples.
In addition, a 12-day flight of the Russian Bion-M2 spacecraft with a variety of living organisms on board has recently been successfully completed. Some flew, again, outside, in a piece of basalt, and, most likely, were able to survive it. Thus, there is little doubt about the ability of some species to survive even in outer space.
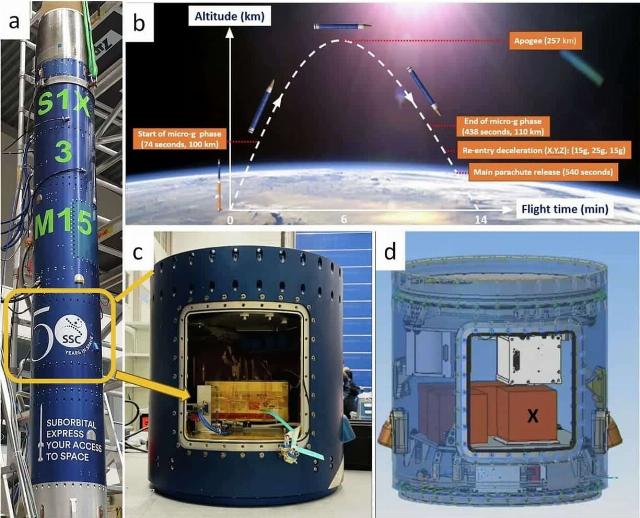
Researchers from Australia and Sweden decided to collect as much information as possible specifically on the tolerance of microbes to overloads during the launch and landing of the spacecraft. To do this, they used the Suborbital Express 3 — M15 suborbital rocket from the Swedish Space Corporation. It was launched in November 2022 with a microscopic "crew" in an airtight container — spores of Bacillus subtilis hay bacillus.
These organisms are known for their endurance to radiation, toxic substances, and almost anything else: in an extreme situation, they turn into a "dormant" spore capable of surviving the harshest conditions.
Hay bacillus is widespread in water, soil, and air, which means it "automatically" gets on spacecraft parts during assembly and preparation for launch. Due to its survivability, even diligent sterilization does not guarantee complete elimination of these spores. By the way, recently a whole "zoo" of mutated organisms was found in the premises of NASA.
As the researchers said in their article for the npj Microgravity publication, the Bacillus subtilis rocket rose to an altitude of 257 kilometers. The flight lasted just over 10 minutes in total. During the launch, the spores experienced overloads of up to 13 g, and on descent — about 30 g. This is much more severe than the conditions for launching and landing manned spacecraft. For example, at the launch of the Soyuz rocket, overloads are up to 7 g, and at the landing of the capsule — 3-4 g. In addition, the descent of the hay stick rocket was unstable, with intense rotation.
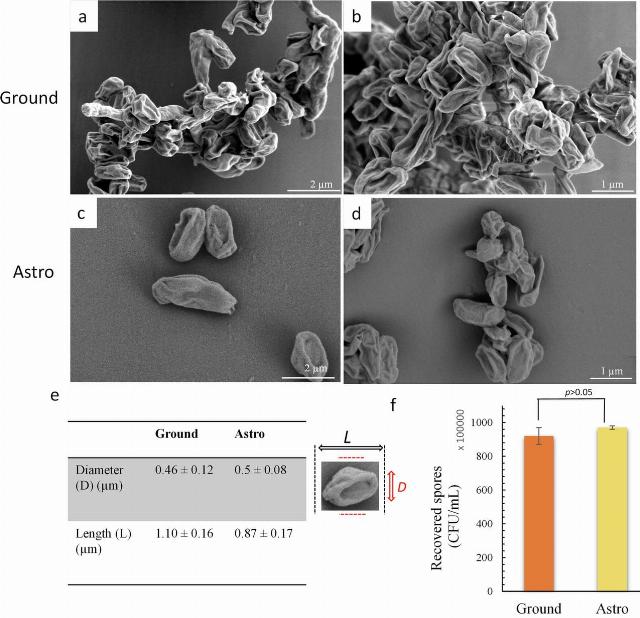
Comparison of Bacillus subtilis samples left on Earth (above) and returned from space (below)
Image source: Eric Yang et al, 2025
For comparison, a similar culture of Bacillus subtilis was left on the Ground in a laboratory. Upon the return of the "space" spores, they were placed in a nutrient medium and watched as they successfully germinated and created new colonies. The number of living microbes turned out to be almost identical to that in the "terrestrial" group.
This allowed us to draw the most important conclusion: some organisms are really capable of carrying everything related to space flight. Not only microgravity, radiation, and airless space, but also extreme overloads. This is again reminiscent of the panspermia hypothesis, which suggests the possibility of bringing life to a planet with falling comets or asteroids.
It is also now clear that unintentional "contamination" of the lunar and Martian surfaces by terrestrial life could well have occurred and even certainly did. So we will have to be very careful in the search for extraterrestrial life: in the case of the long-awaited discovery of living microbes on Mars, we can expect great disappointment with a thorough analysis of these microbes.
Adele Romanova