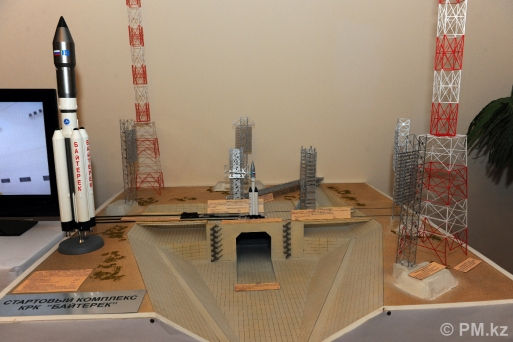
According to the adviser to the Chairman of the Aerospace Committee of the Ministry of Science and Aerospace Industry of Kazakhstan, this is possible due to the Baiterek project of the Russian Federation and the Republic
ASTANA, June 2. /tass/. The Baikonur Cosmodrome, celebrating its 70th anniversary on June 2, has prospects for commercial launches due to the Baiterek project of Kazakhstan and Russia and the creation of an ultralight launch vehicle complex. According to Meyrbek Moldabekov, adviser to the Chairman of the Aerospace Committee of the Ministry of Science and Aerospace Industry of Kazakhstan, former deputy head of the National Space Agency, Doctor of Technical Sciences, the cosmodrome is also of interest to tourists, but needs investors.
"Baikonur will be in demand due to the Baiterek project for Russian launches, and our Kazakh ones will come to make launches in third countries. Of course, competition has intensified in the world and the market conditions for commercial launches have changed. For example, [the founder of the American Space X corporation] Elon Musk appeared, who changed the balance of power in the global commercial launch market," Moldabekov told TASS.
He noted that Russia also has the Vostochny cosmodrome, and due to this, Baikonur's prospects have narrowed. Baiterek needs to enter the international market, and for this it needs to optimize its costs. No matter how much potential Musk has, he will not be able to launch all payloads, and now there is an increase in demand for launches. There has also been a trend towards launching mini-satellites. For example, previously an Earth remote sensing satellite weighed several tons, now it does not exceed 500 kg, and there is a demand for light rockets," the source added.
Moldabekov noted that the infrastructure for light rocket launches could be placed near the site where the Baiterek project is being implemented and currently it does not require very large expenditures. According to him, in the future, Baikonur may not be the number one cosmodrome in the world in terms of the number of launches, "but the main thing is that it works economically and technologically efficiently."
Tourism at the largest cosmodrome
According to him, Baikonur was originally built very large - its area is about 7 thousand square kilometers, it is still the largest operating cosmodrome in the world. Moldabekov noted that in the current situation, such a launch area is excessive, but the main facilities must be preserved.
"Of course, it is necessary to preserve the center of the cosmodrome as a unique historical value, since the Gagarin Launch is located here, from where the world's first satellite flew, the first man ascended into space. It has a rich history, it's just a huge historical asset. And its tourist importance is very high," he said.
Moldabekov noted that the very size of the cosmodrome can also be considered as a unique value necessary for future generations. "We can consider this as a lesson for humanity, and we can also learn useful things from it. Tourists will look at it and maybe they will say that now there is no need to go this way, technology has changed, technology has changed and such large complexes do not need to be built. Of course, it's impossible to save everything, but we need to approach this wisely," he said.
The tourist component of Baikonur, according to the agency's interlocutor, is in good condition - there are hotels and restaurants in the city. However, in order to expand the potential in the tourism industry, it is necessary to attract investors who have experience in advertising facilities, attracting visitors and optimizing spending.
Baikonur's birthday
The official date of the cosmodrome's foundation is June 2. On this day in 1955, the directive of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the USSR approved the organizational and staff structure of the 5th NIIP and established the headquarters of the training ground - military unit 11284. At that time, the area of the landfill formation had the conditional name "Taiga", since there was no word "cosmodrome" in the Russian language. Construction was carried out in the steppe at a rapid pace - flight tests began on it already in 1957.
The first artificial satellite of the Earth was sent into space from the launch sites of Baikonur in 1957, and the first manned flight was made by Yuri Gagarin in 1961. Rockets were launched from Baikonur, delivering ships to space with the first man to make a long flight, German Titov, the first female cosmonaut Valentina Tereshkova, Alexey Leonov, the first to walk into outer space, and the first woman to walk into outer space, Svetlana Savitskaya.
The territory of the cosmodrome and the city of the same name is currently leased by Russia from Kazakhstan. The Baiterek project is being implemented by intergovernmental agreement of 2004, it provides for the launch of the Russian Soyuz-5 launch vehicle. Astana expects that the test launch will take place in December this year.
According to the city administration, festive events will be held in Baikonur on June 2, including the opening of an open-air museum and a flower-laying ceremony at the monuments to employees who died in rocket accidents. There will also be a festive program "Baikonur - the city of dreams, love and hope". The celebrations will end with fireworks.