
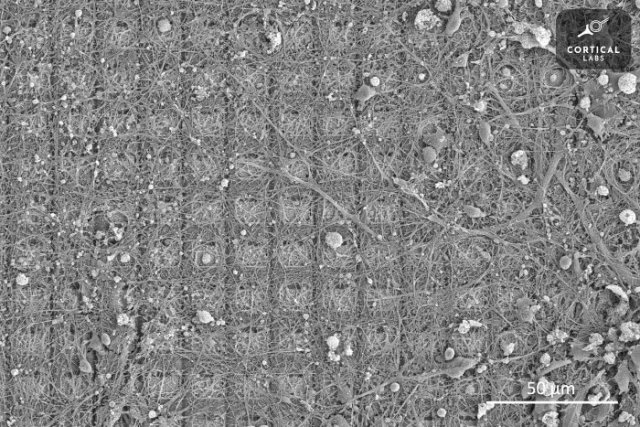
Brain on a chip
Melbourne startup Cortical Labs received 400 thousand dollars as part of a program to sponsor new developments from the National Intelligence Service of Australia. We are talking about the development of the DishBrain project [...], which became a sensation last year. The combination of human and rodent brain cells in combination with an electronic stimulator has become a harbinger of the emergence of a new version of artificial intelligence technology.
Brain on a chip
The Australian military was interested in the potential of a "brain on a chip", since it is neither a brain nor a chip. The living essence of a set of cells allows them to grow, increase their capabilities, develop and, in theory, infinitely improve. They are devoid of the limitations that every electronic device has by default due to its design. At the same time, this brain tissue is neither an organ nor a part of any creature, it is only a set of cells on a substrate that receives nutrition and stimulation to perform various tasks. They will not grow into something individual, they have no instincts, no goals, no tasks, they are relatively easy to manage. And since any form of life is subject to evolution, the Australian military hopes to spur it by forcing the "brain on a chip" to develop at an accelerated pace and grow into something useful.
Alexander Martynenko
