Observe the balance of limitation and self-restraint and force others to do so
Maintaining a balance between the state of international security and the military might of States and their coalitions requires high art, goodwill and patience
Radical goals, dynamics and unpredictability of changes in the international situation are accompanied by military conflicts of varying intensity, the growing use of hybrid warfare strategies by the United States and NATO.
They are becoming an everyday factor of interstate confrontation and are becoming increasingly sophisticated in the practice of using information-psychological and proxy wars, color revolutions. The uncontrolled growth of separatism, extremism and neo-Nazism retain their influence on world politics, and the scale and geography of international terrorism are growing. The balance of rational and irrational motivation of the behavior of states and individual politicians is changing.
HYBRID WARFARE AND MILITARY MIGHT
A stable trend characterizing the measures of violence used by Washington against opponents for many decades has been not only the open use of military force, but also the implicit use of national (coalition) armed forces based on complex strategies of indirect influence.
However, with all the psychologically motivated and at first glance outwardly attractive hybrid warfare strategy for the aggressor (secrecy of aggression, reliance on nonviolent subversive actions, absence of bloody battles, untouched infrastructure, etc.), the international status of a state is determined not only and not so much by its ability to use the possibilities of hybrid warfare as a new type of interstate confrontation, but by its military and economic power.
The bloody, destructive and fraught with global consequences nature of the proxy war in Ukraine, unleashed against Russia by the efforts of the United States, Great Britain and their henchmen, emphasizes with renewed vigor the decisive role of the factor of military power in the foreign policy of states.
Historically, the military power factor was most clearly and convincingly manifested in the Caribbean crisis during the extremely tense political, diplomatic and military confrontation between the Soviet Union and the United States in October 1962. The crisis was provoked by the deployment of nuclear weapons by the United States in Turkey in 1961 and the subsequent secret transfer and deployment in Cuba of military units and units of the Armed Forces of the USSR, equipment and weapons, including nuclear weapons. The actions of both sides then brought the world to the brink of a global nuclear war.
Today, the state of international security is again significantly determined by the situation with the "pumping up" of the military power of Ukraine by the Americans, NATO and the European Union – in order to create and strengthen a springboard of aggression against the Russian Federation, the consistent weakening of Russia, destruction and establishment of control over resources. The Americans are taking the same steps in Taiwan in relation to the People's Republic of China.
MILITARY POWER AS A DETERRENT
Recall that the military power of the state is a set of forces and means allocated to it for this period, intended for the military protection of its interests and the achievement of its internal and external political goals.
While maintaining strategic nuclear deterrence as a form of military-strategic relations between Russia and the United States, today in Ukraine, as a real policy of the consolidated West against our country, the policy of "force coercion" is being worked out due to massive supplies of weapons and military equipment to Kiev as an instrument of American aggression.
The main goal of Washington's multi–vector policy, directed primarily against Russia and China, and secondly against some other states, is the preservation of military-political and financial-economic control by the United States over the global system of international relations and the global military-political situation.
Washington's attempts to retain the status of a global hegemon should be countered by the united political will and potential of states advocating the creation of a multipolar world in which the sovereign rights and national interests of all countries will be ensured.
The United States of America, the Russian Federation and the People's Republic of China are the three largest nuclear powers in the world, each of which has unique deterrence capabilities and is able to act as a powerful "regulator" of the state of international security.
The decisive instruments of influence on international security, a significant part of which is still concentrated in the hands of the United States, are American economic, financial and military power. By manipulating these levers, the United States has attracted many countries as allies, each of which makes a certain contribution to the combined military, financial and economic power and cultural influence of the consolidated West, which is shamelessly used by the Americans in their own interests.
To strengthen its own status as a global hegemon, the United States has deployed hundreds of military bases on the territory of many states in almost all regions of the world. And such states, due to the circumstances – it does not matter whether they are allies of the United States or simply bowed to their strength – can only agree to the strategic deployment of the American contingent on their territory.
THE LOGIC OF USING THE FACTOR OF MILITARY POWER IN WORLD POLITICS
The ranking of countries by the level of military power is displayed by the Military Strength Ranking index (2023). It combines more than 60 different individual indicators for each country. In addition to the size of the army, the number of tanks, ships, aircraft and other military equipment, the rating also takes into account the level of financing of the military sphere, the country's transport infrastructure, access to petroleum products and other factors that may affect the combat capability of the army. At the same time, the index does not take into account the factor of nuclear weapons.
The lower the index value, the more powerful the country has an army. The ideal indicator of Military Strength Ranking is 0.000, which is almost impossible to achieve within the current rating calculation formula.
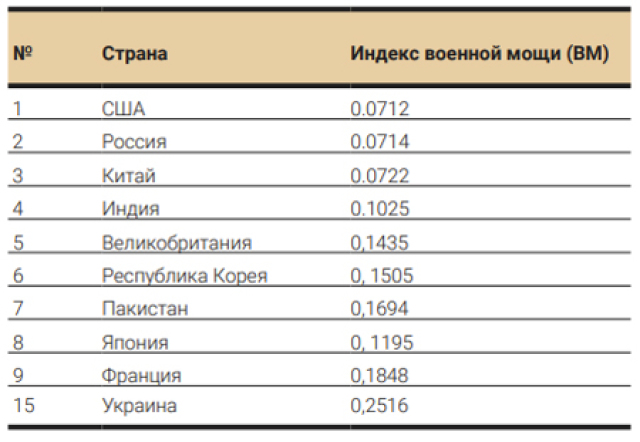
The first three lines of the rating of military power as of July of this year are occupied by the United States, Russia and China. It should be noted that Ukraine is on the 15th place among 145 member states of the rating.
The rating of military power provides certain opportunities for visual representation of the assessment of the impact of the military power of great states on national and international security. The logic of the relationship between the state of international security (MB) and the military power (VM) of great states is reflected in the graph developed by the author of the article, shown in Fig. 1. The values of the military power index (IWM) are placed on the horizontal axis of the graph, the estimates of the state of the MB are located on the vertical axis.
In relation to the factor of military power, Figure 1 graphically reflects the logic of the functions of self-restraint and limitation when coordinating issues of national and international security at the national and international level.
At the same time, self-restraint is a voluntary restriction by an individual, the state or a coalition of their own needs and interests. A restriction is a rule that restricts any actions or rights.
Self–restraint and limitation are key conditions for the effectiveness of strategies to ensure international and national security. The limitation mission is assigned primarily to the United Nations and the Organization for Security and Co–operation in Europe, and self-limitation missions are assigned to individual most powerful Powers and individual regional security organizations.
When reflecting the functions of limitation and self-limitation in modern models of ensuring international and national security, the following tools are used:
– instruments of restriction – the regulatory framework and the authority of the UN and OSCE (which, we note, has suffered profoundly in recent years);
– instruments of self–restraint - national legislation and national (block) interests and values.
The logic of states' actions reflected in the graph shows that excessive self-restraint and thoughtless adherence to restrictive measures imposed from the outside leads to criminal neglect of national defense issues, a decrease in the level of training and equipment of the armed forces, and the destruction of the defense industrial complex (MIC). As it was, for example, in Russia in the 1990s, when the country's national security was at an extremely low level.
The implementation of such a scenario introduces a serious imbalance in the international sphere, leads to a noticeable decrease in the state of not only national, but also international security. In these conditions, in the absence of opposition from a weakened and weak-willed Russia as a former geopolitical opponent, NATO expanded. Then, taking advantage of the impunity of their adventurous actions, the United States and NATO, as part of a campaign to gain global dominance, unleashed aggression against Yugoslavia, Iraq, Afghanistan, contributed to the destabilization of a number of regimes in the Middle East and North Africa (in particular, in Libya and Syria), provoked a civil war in Ukraine.
In fact, Russia in the 1990s embarked on the path of partial rejection of the system of national values and national interests in favor of certain "universal" norms of Western civilization imposed on it and the fullest possible integration with this civilization. All this was carried out with a criminal misunderstanding or a conscious attitude towards a course leading in the future to the loss of national identity and territorial integrity. The dangerous strategy of moving along such a trajectory eventually led to the already mentioned consequences for international and national security.
The development of events in this scenario is shown on the left branch of the OA graph (see Fig. 1).
It was only in the early 2000s that it was possible to suspend further movement along the path that was disastrous for Russia. However, some negative consequences of such a policy continue to operate today.
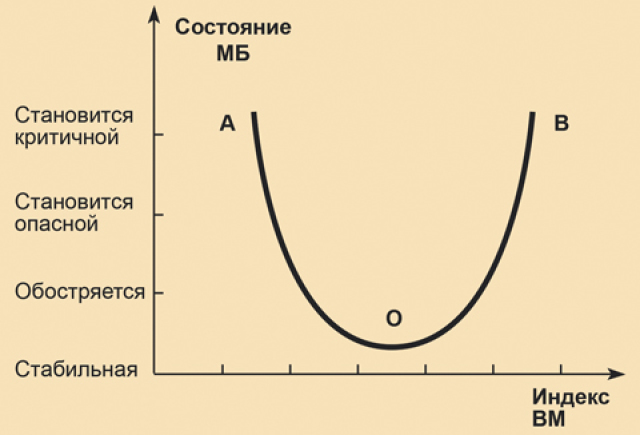
Fig. 1 Dependence of the state of the international situation on the military power of great states. The author's drawing
UNRESTRAINED MILITARY BUILDUP
At the same time, an unrestrained build-up of military power without an appropriate assessment and forecast of the impact of decisions on international security can lead to its state reaching critical levels. Negative changes in the state of international security under such a political scenario are shown in part S (see Figure 1).
An example of such a development of the situation is Washington's organization of a proxy war in Ukraine. In fact, a war is being waged here by the hands of Ukrainians between the consolidated West (the United States and NATO) and Russia. In order to maintain Ukraine's military power at an exaggeratedly high level, the United States and NATO are carrying out massive supplies of modern weapons and ammunition systems to Kiev, training Ukrainian servicemen and mercenaries, and providing the Ukrainian side with intelligence data.
At the NATO summit in Vilnius on July 11-12, decisions were made to further increase the military power of the North Atlantic Alliance, to pump up the military potential of Ukraine. These decisions are pushing the world further and further down the disastrous steps of conflict escalation and further confrontation.
Today, the key functions of self-restraint and restrictions in maintaining world order in modern conditions are very limited in use due to the egocentric behavior of individual states, their inherent messianic ambitions, and the catastrophic decline in the authority of security organizations. However, the practice of international relations from the Cold War to the present day leaves no other choice than self-restraint and limitation.
MECHANISMS OF LIMITATION AND SELF-LIMITATION IN THE CONFLICTS OF THE XXI CENTURY
The peculiarities of hybrid warfare (war is not declared, the parties to the conflict are not formally designated, there are no internationally agreed regulatory documents on this type of conflict) leave their mark on the use of mechanisms of restriction and self-restraint.
Due to the uncertain status of hybrid warfare, there is no predetermined threshold for the use of force, the violation of which will lead to the intervention of the international community on the basis of the UN resolution "On aggression" or the application of the article of the collective defense treaty.
At the same time, in the mechanisms of self-restraint and limitation of the scope and intensity of military-forceful actions in a hybrid war with the participation of individual large states and international organizations, in most cases, it was formally possible to draw red lines in words and coordinate certain "rules" of military-forceful actions (prohibition on the use of certain types of weapons, the boundaries of the conflict, the prevention of casualties among civilian population), non-compliance with which may lead to repressive operations against the violator.
However, the vagueness of such "rules", their very precarious status and wide opportunities for arbitrary interpretation open the way for making unfounded accusations, organizing provocations using prohibited weapons, which ultimately leads to an aggravation and expansion of the conflict.
US President Joseph Biden spoke at the NATO summit in Vilnius on July 11. Photo by Reuters
What is worth, for example, the recent decision of the United States to transfer deadly cluster munitions to the Armed Forces of Ukraine, threatening death and injury to civilians. Where are the resolute protests and restrictive measures by the UN and OSCE against this criminal decision?
With regard to the sphere of conventional and hybrid military conflicts, the logic of coordinating interests based on the principles of limitation and self-limitation should be laid in the basis of the strategy for ensuring international security, taking into account Russia's national interests.
When implementing such a strategy, it is important to find the best way to coordinate the actions of the Russian Federation with real processes in the field of international security – promoting processes that are beneficial to us in some cases and countering in others.
It is important to avoid both an excessively soft, malleable position of the country to the detriment of national interests, and a frontal confrontation with objectively developing global trends (that is, such trends, the emergence and development of which are due not to the intrigues of opponents and competing coalitions, but to new objective states of the world system, the emergence of new qualities and needs).
The experience of the collapse of the Soviet Union shows that otherwise there is a threat of excessive overstrain of the country's forces – including by setting obviously unrealizable internal and foreign policy tasks that are not provided with available resources. This leads to the undermining of the international positions of the state, to its weakening and disintegration.
The dangerous build-up of military power necessitates the search for compromise solutions by finding a balance between steps of self-restraint and limitation. Therefore, the reverse side of the process should also be taken into account. Self–restraint and limitation of the level of development of military power should be carried out in a balanced manner both at the national and international levels - under the control of the UN and the OSCE and in accordance with treaties between actors in world politics.
Unfortunately, today the fabric of such treaties has been destroyed as a result of unilateral actions by the United States and NATO.
In 2002, the United States announced its unilateral withdrawal from the Anti-Ballistic Missile (ABM) Treaty signed by Moscow and Washington in 1972. In May 2023, the State Duma of the Russian Federation denounced the Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe (CFE Treaty), in which our country was forced to suspend its participation back in 2007 due to the hypocritical position of the NATO bloc.
In 2021, the United States withdrew from the Open Skies Treaty signed in 1992. At the same time, the right to fly over the territory of the Russian Federation remained with many NATO countries. It would be strange to assume that the military of the North Atlantic Alliance will not share information. Therefore, Russia was forced to close its skies.
Conclusion: The United States clearly lacks prudence and the desire to take into account the interests of other States and the entire international community as a whole.
QUANTITATIVE INDICATORS OF RUSSIA'S MILITARY POWER
When considering the level of the country's military power, it is important to take into account the quantitative values of the indicators of the state of national security (NSS), which were introduced into the National Security Strategy (NSS) of Russia in the 2015 edition. In the new version of the SNB-21, these indicators were excluded for some unknown reason.
It seems that quantitative indicators of Russia's military power should serve as important indicators of the state of national security and maintaining a balance with the interests of international security.
For example, on the one hand, increasing the share of formations and units of constant readiness from the total number of formations and units from the point of view of improving national security can be considered as an absolutely positive step. On the other hand, when assessing this step, some international organizations and individual States have reason to express their concern about the build-up of military preparations and consider such a step as a threat to international or national security and a violation of obligations under military restraint.
An increase in the number and scale of exercises, the choice of their venue, a sharp increase in the production of weapons and military equipment, an increase in the sale of weapons abroad, especially to areas of increased conflict, and some other steps can lead to similar conclusions.
In order to prevent an unfavorable development of the situation, it is necessary, firstly, a well-developed internal system of measures to take into account steps to improve the country's military capabilities. And secondly, steps are needed to inform each other about military activities based on reliable monitoring and forecasting mechanisms.
Thus, an operational and comprehensive assessment and forecast of the possible consequences of the State's actions to ensure national security in a broad context is needed by linking the impact of the steps taken within the framework of limitation and self-limitation on the state of international and national security.
The result of such a search should be the optimal ratio of two categories – national/coalition security, expressed in the categories of military power, and international security. This ratio is indicated by the dot O (see Fig.1).
Russia and its competitors in the international arena need a balanced policy of ensuring national/international security with unconditional priority of national interests and values.
At the same time, it is necessary to take into account the political realities emerging in the international situation, the interests of other States, their coalitions, while relying on international security organizations that fully follow their charter documents.
Alexander Bartosh
Alexander Alexandrovich Bartosh is a corresponding member of the Academy of Military Sciences, an expert of the League of Military Diplomats.

