NASA has approved the start of development of the preliminary design of the NEO Surveyor infrared space telescope, which will go into space in 2026. It is expected that in 12 years of operation, the telescope will help bring the number of known potentially dangerous near-Earth asteroids with a diameter of more than 140 meters from 40 to 90 percent of their total number in this size range, according to the NASA website.
The principles of protecting the Earth from potentially dangerous objects, such as asteroids and comets, require that a celestial body be discovered at least a few years before a possible collision with our planet. This requires the development of increasingly sophisticated ground-based and space-based systems for continuous tracking of near-Earth objects and the compilation of the most complete catalog of such bodies. In particular, NASA in 2005 [...] set a goal to detect 90 percent of near-Earth objects larger than 140 meters and to date has found about 40 percent of such asteroids, using both ground-based sky surveys, such as Pan-STARRS or CSS, and space-based observatories, such as WISE or Spitzer.
The project of the new NEO Surveyor space telescope was first proposed for implementation in 2006, but only in 2019 it was approved . It is assumed that the infrared telescope with a mirror diameter of 50 centimeters will conduct observations of near-Earth space, being in a halo orbit around the first Lagrange point in the Sun-Earth system. The field of view of the telescope will be 11.56 square degrees, it should work for 12 years and during this time find and determine the properties (albedo and diameter) of the vast majority of potentially dangerous near-Earth asteroids and comets, ranging in size from several tens of meters or more. For best performance, the telescope will be equipped with a sun shield and a passive cooling system for detectors up to 30 kelvin due to radiation into the surrounding space.
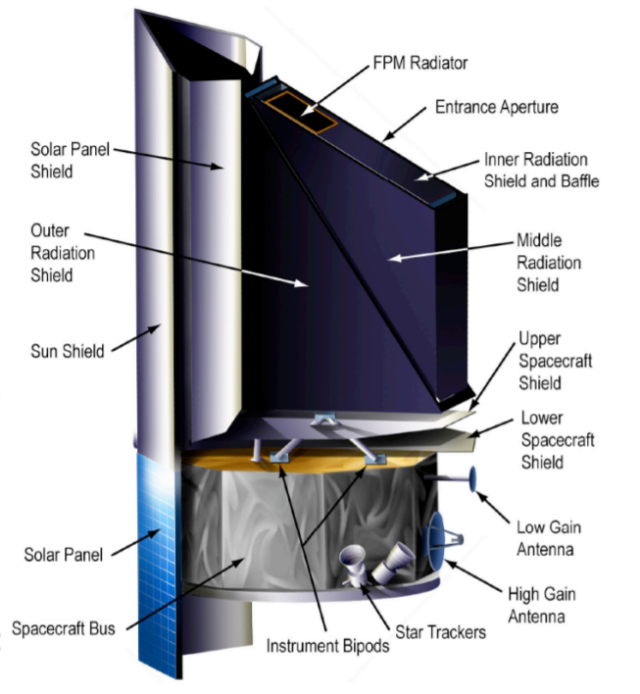
Image source: NASA
In early June 2021, NASA completed the review of the project review and approved the transition to the development of the preliminary design of the telescope, which will be handled by the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The launch of the telescope into space is scheduled for the first half of 2026, and the Atlas 5 or Falcon 9 can act as a launch vehicle.
Earlier, we talked about how astronomers postponed the meeting of the famous asteroid Apophis with the Earth for a hundred years, and you can check whether a potentially dangerous asteroid was named after your city in our material "Globe of Surgut" .
Alexander Voityuk